Blog
4 Key Findings From Our Inaugural Redis Digital Transformation Index Report
Digital transformation has been an ongoing journey for many organizations across industries for the past few years. However, this transformation was significantly accelerated this past year due to COVID-19.
Since people’s day to day lives have become more digital, their expectations—not surprisingly—have grown much more real-time in nature. And having access to real-time data is a key component for all organizations to ensure they can deliver the best experience to their users.
As the builders of a real-time data platform, we find ourselves at the center of many digital transformation projects. We believe that for organizations to be successful in their journey, they need to have both a digital mindset and the right toolset.
Today, we are happy to announce the release of the first Redis Digital Transformation Index e-book. In this report, we are introducing a new composite index to highlight the maturity level of 550 AWS re:Invent survey respondents with respect to their use of technologies such as the cloud, microservices, containers, and NoSQL databases. We asked respondents how prevalent each of these technologies are in their stack and their plans for the future.
Furthermore, the survey covers other topics such as caching strategies, types of databases, tolerance for downtime, factors for choosing a database and more. You can read the whole report, but read on for a quick rundown of the most interesting results:
1. Cloud is the leading driving force in digital transformation
For the purposes of this survey, we created a composite metric called the Redis Digital Transformation Index (DTI). We combined participants’ descriptions of their strategies toward the cloud, microservices, containers, and NoSQL databases. The adoption of these technologies is a good indicator of an organization’s progress in its digital transformation journey.
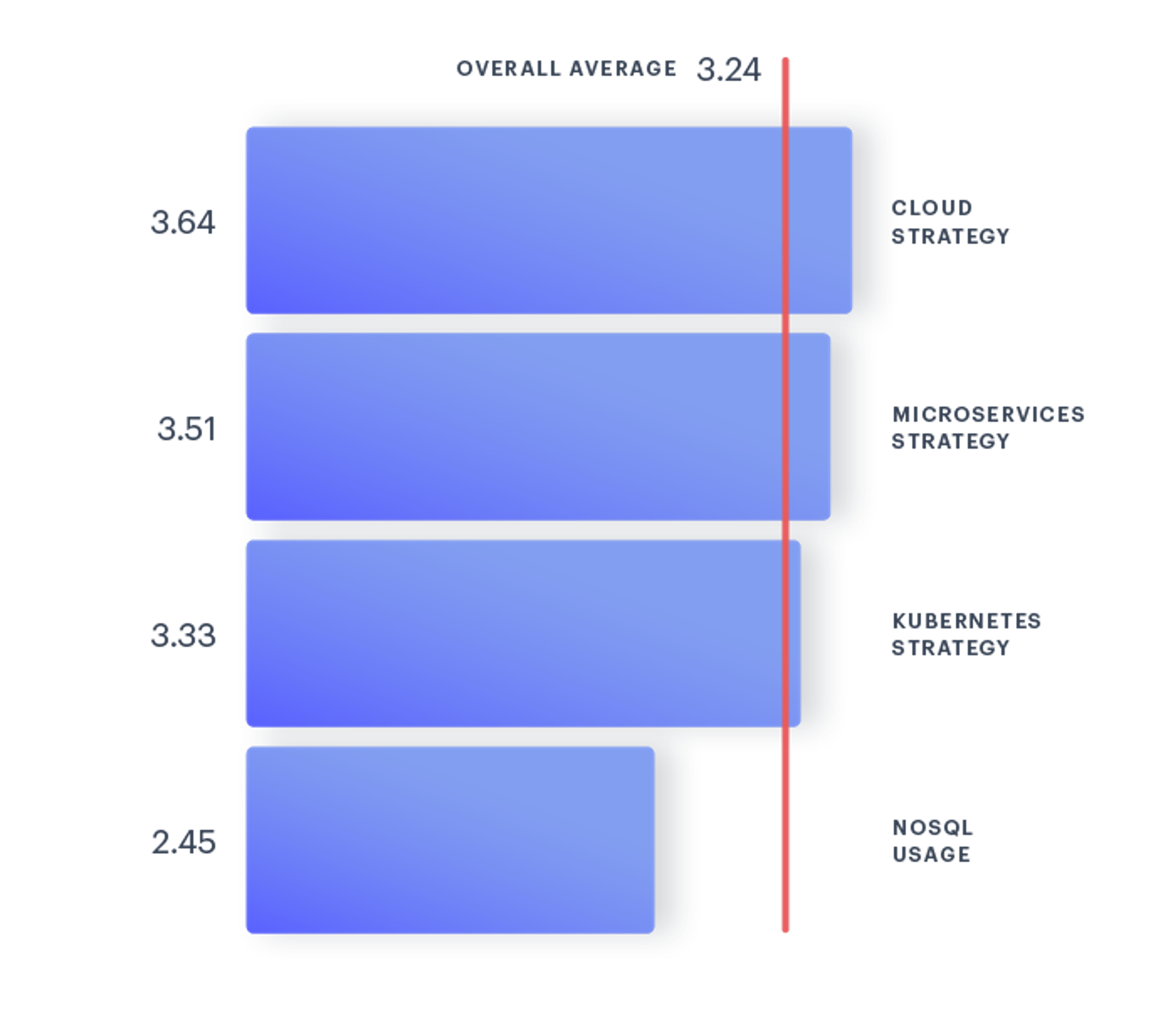
By looking at each component of the DTI, the data shows cloud strategies to be the most mature with an average of 3.64 out of 5. NoSQL database strategies came in last at 2.45, with the composite DTI for all participants at 3.24.
2. No tolerance for downtime
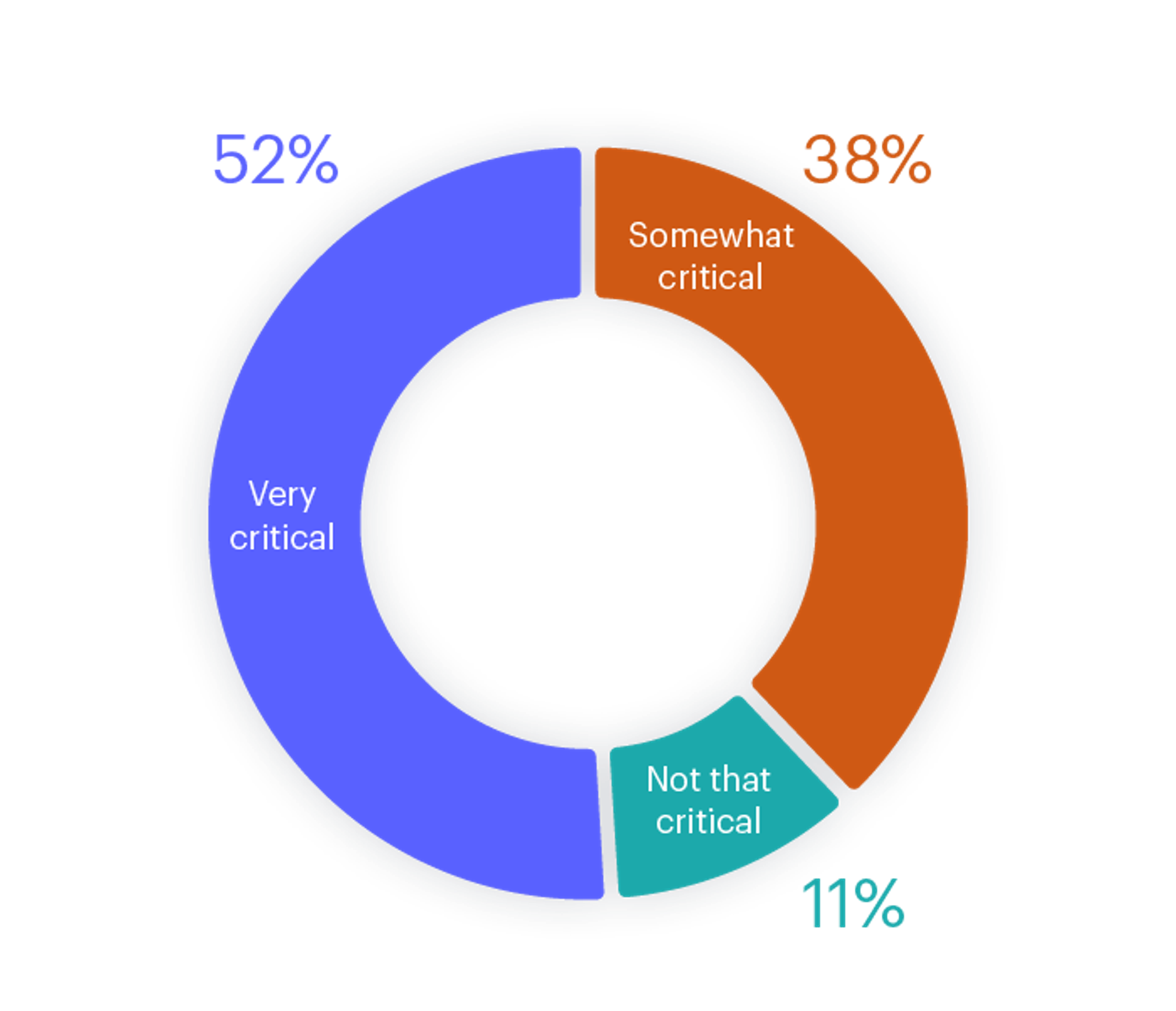
In a world where we are more connected than ever, limited downtime can range from an inconvenience to hugely disruptive. So we asked our respondents to rank their tolerance regarding downtime in cache and database. Understandably, responses varied across the industries, but on average, 52% stated that they can’t afford any downtime either in database or cache. 38% responded that while they can tolerate limited downtime in cache, downtime would be unacceptable for their database. Finally, 11% said they can handle limited downtime since their application isn’t customer-facing.
3. Caching is crucial for relational database users
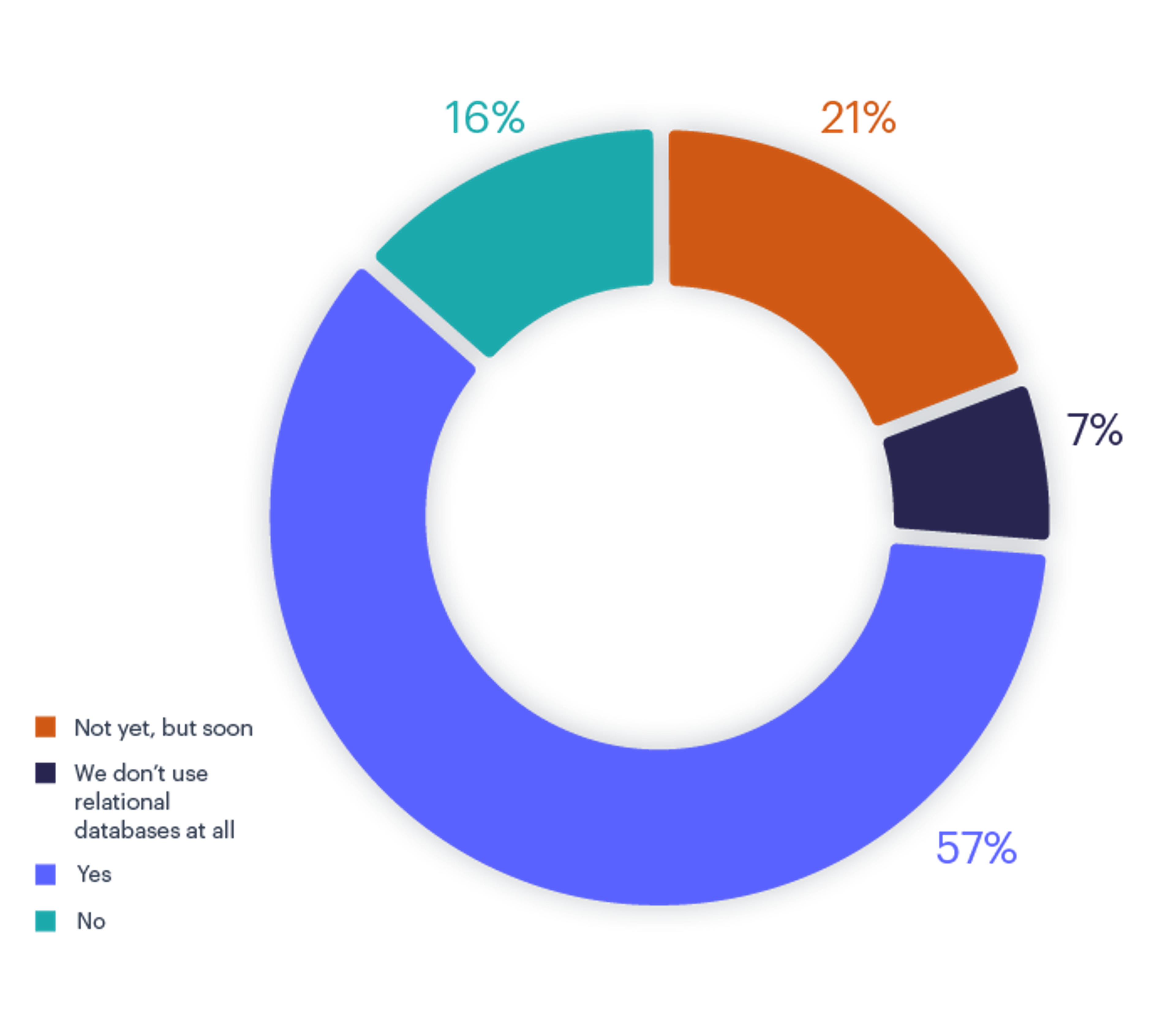
Caching is a widely used approach to improve an application’s performance and scalability. Our survey shows that 78% of respondents are either currently using caching or plan to do so soon. For the majority of respondents that use relational databases in their technology stack, having a highly performant and scalable caching layer is simply non-negotiable.
4. Key-value databases are almost as common as relational
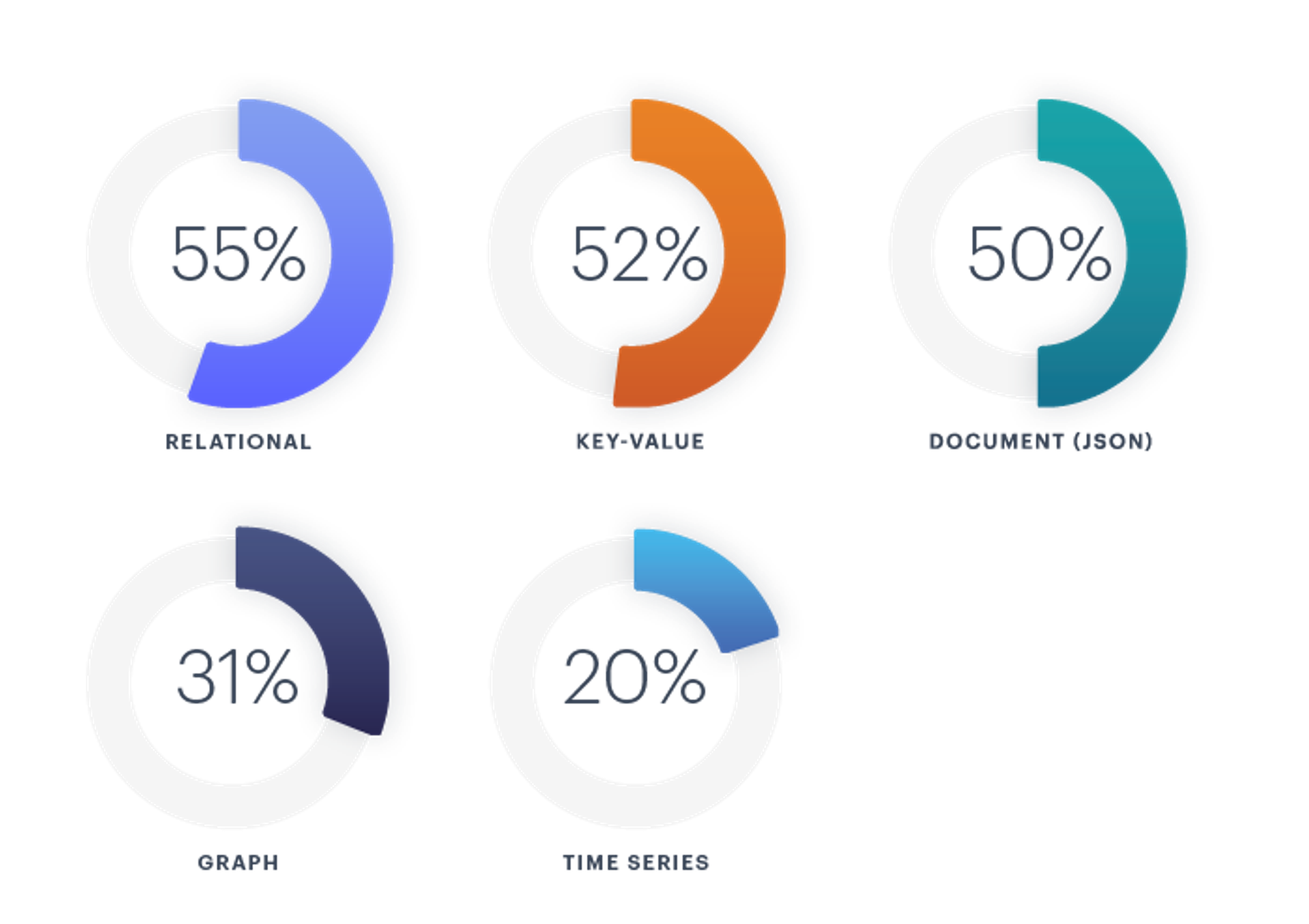
When asked how many types of databases respondents use in their organization, the average number is two. Relational databases have been a dominant technology for decades, so it’s not a shock to see them take first place (55%). NoSQL databases are much younger in comparison. We were pleasantly surprised to see key-value databases coming in a close second at 52%. This shows that NoSQL databases are both widely adopted and an essential component of the majority of organizations’ data management systems.
This survey demonstrates that organizations across industries are adopting a multitude of technologies and strategies to achieve their digital transformation goals. The full report contains details regarding DTI across industries, top factors when choosing a database per industry, popular languages for developing database applications, and whether users of tabs or spaces are the early adopters of new technologies.
Get started with Redis today
Speak to a Redis expert and learn more about enterprise-grade Redis today.
