Blog
How to create a powerful drone system using Redis to protect crop insurers from false claims
In the face of climate change, crop insurers are faced with a whole new range of problems. A lack of data to assess cultivable land and yield has always been an issue, but accurately estimating crop damage has also proven to be almost an impossible task.
To compound this even further, the remote location of crops can prevent insurers from finding specialists to carry out inspections and risk assessments. These all have implications on cost and time to insurers.
But the capabilities of drones are fast being recognized as the solution to these problems.
A Launchpad App demonstrated how this could be achieved by creating an interconnected drone system that uses Redis to transmit data between components. Redis pulled each component closer together, enabling reams of data to be transmitted in real time.
With this asset, drones were able to fly over fields, take images of crops, then send them back to an online portal for assessment. A demo was created to illustrate how this was achieved.
Let’s investigate how the team managed to achieve this. But before we go any further, we also have a great variety of different apps for you to explore, so make sure to check them out on the Launchpad.
Contents
- What will you build?
- What will you need?
- Architecture
- How does it work?
- Getting Started
- How to set up the Backend
- How to set up the Frontend
- Conclusion
1. What will you build?
You’ll build a drone system which uses Redis and cloud technologies that captures accurate data of crops in rural areas at speed. Crop insurers can leverage this asset to create more secure insurance policies whilst maximizing transparency during the claims process.
We’ll explore how they managed to tie in all of these different components to work harmoniously with one another.
2. What will you need?
Development
- Next.JS: enables React based web applications functionalities such as server-side rendering and generating static websites(portal)
- Python: used as the preferred programming language
- Java/Spring Boot:used in building microservices that handle all customer-related queries, policy and claims-related API
Cloud and services
- Azure cloud: stores the analyzed images to Azure Blob Storage
- RedisGears: used to listen to the image stream
- RedisAI: executes deep learning/machine learning models to manage data
- Redis Streams: starts the drone when the inspection is triggered by the user on the frontend.
- RedisTimeSeries: provides time series data
- Docker container: processes and analyzes images using RedisAI, Tensorflow and custom vision service.
- Microsoft Airsim: a simulator for drones
- Custom Vision Service: creates a custom computer vision model
- Customer-Service: handles all customer related queries
- Policy-Service: handles policy and claim related API
- Inspection-Service: contains all API related to Inspection
3. Architecture
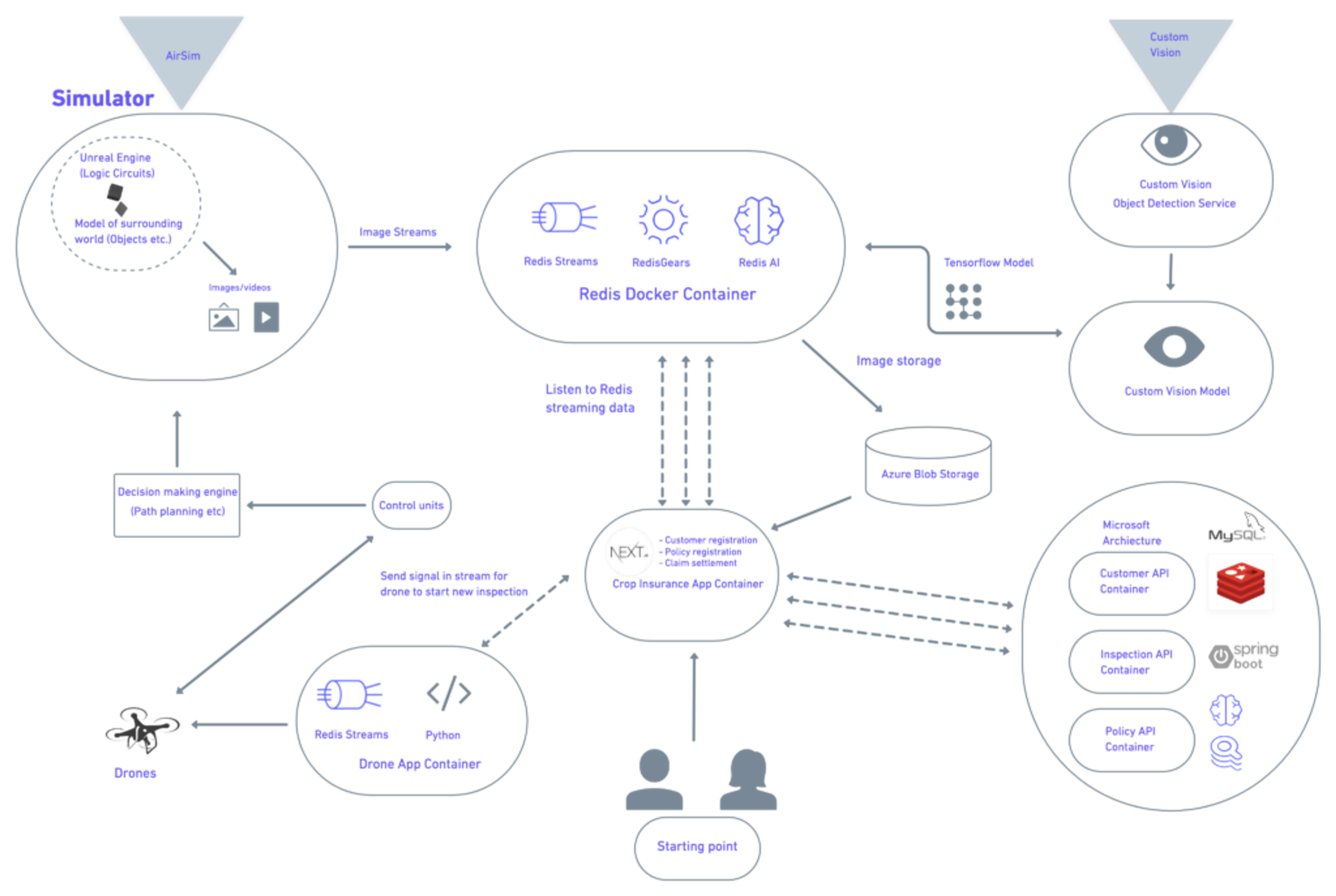
4. How does it work?
Now let’s have a look at the architecture. To simplify things we’ve broken it down into 4 sections.
The portal
- A portal is created for crop insurers where they’re able to complete the registration of their customers along with their policy and claim settlement. The insurer has the ability to live scan their customer’s land from this portal.
- Once the user clicks on the live inspection, a unique ID will be generated and passed through Redis Streams.
- The drone app container receives this message and sends it to the drones which then take flight.
AirSim
- The virtual land (see above image) is created using an AirSims simulator which sculpts the virtual crops.
- Drones will fly over the land to capture images of crops which are transmitted in real-time to Redis via Redis Streams.
Custom Vision
- A pre-trained model was created using the Microsoft custom vision service which can identify different types of objects in the images e.g high-crop land, low-crop-land, fertile-land etc
- The Tensorflow Model is passed onto Redis where Redis AI will take the raw images from the drone and will convert all of the images into the modelled images.
- These modelled images are stored in the Azure Blob storage. Redis Streams is used to transmit these images to the frontend app which will show all of the data of this inspection.
- Once the drone has finished scanning the crops, the data will be sent to the backend system using a microservice architecture
The Microservice Architecture
- The microservice architecture is divided into 3 different containers: Customer API, Inspection API, and Policy API
- This microservice architecture is built on the Java Spring Boot framework using Redis, RediSearch, and RedisJSON.
- The backend API will inspect all of the data. Based on this data, the sum assured and the premium will be calculated and passed onto the frontend app. From here, the insurer and the farmer can agree on a new insurance policy.
Thanks to this product, the insurer can carry out crop inspections in real time and create an insurance policy from his/her office.
Getting Started
Step 1. Clone the project repository:
If you look at the source code repository, the whole project is divided into 3 major sections:
- Redis_Airsim:
- RedisMod for loading Redis modules
- Image modelling using RedisAI
- Stream Registration using RedisGears
- Modules to create virtual farm using Unreal Engine objects
- Azure blob storage integration
- Frontend:
- Front end app code
- Integration with Redis stream
- Integration with microservice
- Microservices:
- Microservice code- Java Spring Boot framework
Step 2. Examine the Airsim Simulator
Redis modules, RedisGears, RediStreams, and RedisAI were each deployed in this project. They were all used to analyze images of the land that were captured by the drone in real-time as well as calculating the percentage of different categories in those images using Tensorflow, Microsoft Custom Vision, and RedisAI.
To connect to the AirSim simulator, simply use the Python-based code below. This also allows you to set the coordinates that will determine the path your drone will follow during its flight.
Step 3. Installing the required software
Before executing the Python script, you should install the prerequisite software discussed below.
- Docker
- Docker-Compose
- UnReal Engine(>= 4.24)
- Python(>=3.6)
You can install Docker in your environment by using this link. Also, make sure that you have Docker compose installed in your system.
Step 4. Setting up Unreal Engine
Unreal Engine is the world’s most open and advanced real-time 3D creation tool. At this point, it’s required that you set up the Unreal Engine on your local machine to simulate the flying of drones on virtual fields.
Here are the hardware requirements to set up the Unreal Engine:
- Operating System: Windows 10 64 bit
- Video Card/DirectX Version: DirectX 11 or DirectX 12 or NVIDIA compatible graphics card
- RAM: 32 GB
Once the Unreal Engine is set up on your local environment, you need to download the folder from Google drive. It includes the maps of the different landscapes that the drones will fly over. We’ve placed the folder inside Google Drive due to its large size.
Once the folder is downloaded, you’ll need to double click the ‘FinalProjDroneSquad’ file as shown below:
This will launch the landscape on Unreal Editor as shown below:
Click on the ‘Play’ button as highlighted below to start level 1.
To change the level of the game, first navigate to the Content -> Maps folder. Double click on the Level 2/Level 3 files as shown below and click on the play button.
Thereafter you can proceed to the installation section to set up other prerequisites.
Step 6. Install the dependencies
From the root folder of this project, run the below docker command:
docker-compose up
As you can see from the docker-compose file above, this project combines several Redis modules, such as RedisGears, RediStreams, and RedisAI. These are all used to analyze the images of the land captured by the drone in real-time as well as calculating the percentage of different categories in those images using Tensorflow, Microsoft Custom Vision and RedisAI.
Essentially, this will create two containers that are used in this project on your machine:
- Redis container: hosts RedisAI, Redismod and RedisGears
- Drone App container: initializes the model on RedisAI and registers the stream using RedisGears. It will be in the exit state.
Finally, we need to create the blob storage account to store the analyzed images that are generated using RedisAI. To achieve this, create the container inside the blob storage with the name ‘droneimages.’
cd redisedge\secrets
Copy the connection string from the azure blob storage account and paste it on the ‘azureblobsecret’ file inside the folder.
Step 7. Running the Demo
Open your favorite terminal and run the following commands.
On the first tab run the command below and change the level arguments as 1, 2 and 3 to be able to initiate different levels of the game.
python flyDrone.py –level=1
This will initialize the drone and place it into ‘waiting to take off’ mode.
On the second tab run the command below. This will listen to the inspection carried out by Redis Streams. Data is entered from the front end whenever the inspection is triggered.
python captureImagesFromDrone.py –level=1
Once the data arrives on Redis Streams, the drone will take off and start to capture images. These are then processed and analyzed by RedisAI using Tensorflow.
Note: After changing the level of the game on the Unreal Editor as mentioned, run the above two scripts on a different terminal once again and close the existing ones.
Output
Below are the output images generated by RedisAI.
| Cultivated land with others category | High quality with low quality category |
|---|---|
| Infertile land category | Others category |
|---|---|
6. How to set up the Backend
The backend system is built using microservices that are divided into different entities such as :
- Customer-Service: handles all customer related queries
- Policy-Service: handles policy and claim related API
- Inspection-Service: contains all api related to Inspection
These microservices are built using the Java Spring Boot framework, which, in-turn, uses Redis, RedisJSON, and RediSearch. The backend API will perform all the inspection of data. Based on this data, sum assured and premium gets calculated and passed to the frontend app.
7. How to set up the Frontend
Let’s examine the code which will help you create a public app that can be accessed by a crop insurer.
Steps to run application
Note: Need Node Version 14+
- Clone the repo to the local repository.
git clone https://github.com/redis-developer/CropInsurer
- Install yarn global with
npm i -g yarn
- Run command:
yarn install
- Run Command:
yarn start
- Open http://localhost:3000 in the browser to launch the frontend application.
Portal Credentials
Username: [email protected]
Password: admin
Application Screenshots
Below are screenshots of the application.
Login page
Customer Registration page
Customer List page
Inspection page
Conclusion: Removing barriers with real-time data
Through the advanced capabilities of Redis, this Launchpad App created a powerful drone system which enables crop insurers to scan, monitor, and assess the quality of farm yields from their office. Yet the real asset that brought the project’s ambitions to life was Redis’ ability to provide real-time data.
Transmitting data from A to B at such speed enables the components to work seamlessly with each other in a system that has a complex architecture. Crop insurers can now carry out accurate crop-quality assessments whilst ensuring a more transparent claims process.
To discover more about this innovative project, check out the full app on the Launchpad.
Also, make sure to have a browse around the exciting range of applications that we have there.
Who created this app?
Piyush Jain
Piyush has over 16 years worth of experience in software development and currently works as a solution architect at Publicis Sapient. Make sure to check out his GitHub profile to see all of his exciting work.
Get started with Redis today
Speak to a Redis expert and learn more about enterprise-grade Redis today.