Blog
What is semantic caching? Guide to faster, smarter LLM apps
LLM API costs have a way of sneaking up on you. One month you're running a promising chatbot prototype, the next you're staring at an invoice wondering how your users consumed that many tokens.
A huge chunk of those costs come from repetitive queries. Users ask the same questions constantly, just phrased in different ways. "What's your return policy?" "How do I return something?" "Can I send this back?" Same intent, same answer, but traditional caching can't help because it only matches exact strings. Every variation hits the LLM as a fresh request.
Semantic caching changes this. Instead of matching queries word-for-word, it understands meaning. Questions that ask the same thing, even with completely different wording, return the same cached response. Costs drop and your app gets faster without sacrificing accuracy.
This article covers how semantic caching works, why it outperforms traditional caching for LLM apps, the key benefits it delivers, and best practices for getting it into production.
What is semantic caching?
Semantic caching interprets and stores the semantic meaning of user queries, allowing systems to retrieve information based on intent, not just literal matches. This method allows for more nuanced data interactions, where the cache surfaces responses that are more relevant than traditional caching and faster than typical responses from Large Language Models (LLMs).
Semantic caching works by converting queries into vector embeddings (typically 768 or 1,536 dimensions) and measuring cosine similarity between vectors. When similarity exceeds a threshold (commonly 0.85-0.95), the system returns the cached response instead of calling the LLM.
Think of semantic caching like a savvy librarian. Not only do they know where every book is – they understand the context of each request. Instead of handing out books purely by title, they consider the reader’s intent, past readings, and the most relevant content for the inquiry. Just like this librarian, semantic caching dynamically retrieves and supplies data that’s most relevant to the query at hand, making sure each response matches the user’s needs.
Make your app’s data handling faster, boost performance, and cut costs with LangCache, our fully-managed semantic caching service.
Key components of semantic caching
How semantic caching works
Semantic caching follows a straightforward process that turns user queries into meaningful, reusable data. Here's what happens under the hood:
- Embedding–When a user sends a query, the system converts that text into a vector embedding: a numerical representation that captures the query's meaning. Two questions phrased differently but asking the same thing will produce similar vectors.
- Similarity search–The system compares this new vector against vectors from previous queries stored in a vector database. Instead of looking for exact string matches, it measures how close the vectors are in meaning.
- Cache hit–If the system finds a stored vector that's semantically close enough to the incoming query, it returns the cached response instantly. No LLM call needed.
- Cache miss–If no match meets the similarity threshold, the query goes to the LLM. Once the model generates a response, the system stores both the query embedding and the response in the cache for future use.
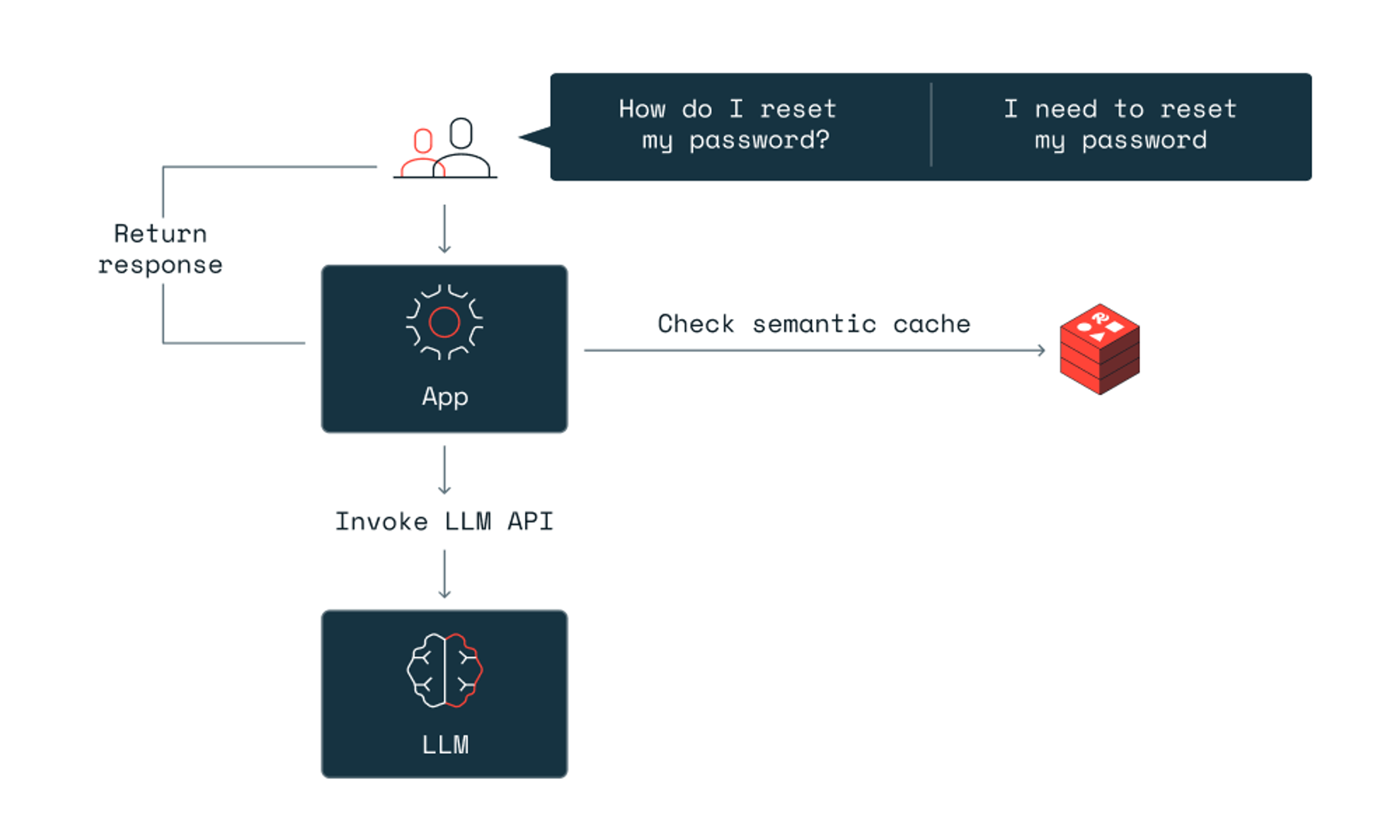
This process means "How do I reset my password?" and "I want to reset my password" can return the same cached answer, even though the words are completely different.
Comparing semantic caching vs traditional caching
Both caching approaches store data for faster retrieval, but they work in fundamentally different ways. The right choice depends on your query patterns and how much variation you expect in user inputs.
| Traditional caching | Semantic caching | |
|---|---|---|
| Matching method | Exact string match | Vector similarity (meaning-based) |
| Cache hit requirement | Query must be identical | Query must be semantically similar |
| Handles rephrased queries | No | Yes |
| Setup complexity | Lower | Higher (requires embedding model) |
| Best for | Static content, API responses, database queries | LLM apps, chatbots, search systems |
| Infrastructure | Key-value store | Vector database + embedding model + cache |
For apps where users ask the same thing in different ways, semantic caching dramatically improves hit rates. Traditional caching still works well for predictable, repeatable queries where the input doesn't vary.
Making LLM apps fast–the impact of semantic caching
Semantic caching is a solid choice for LLM-powered apps. LLMs process a wide range of queries requiring fast, accurate, and context-aware responses. Semantic caching improves performance by efficiently managing data, cutting down computational demands, and delivering faster response times.
One example is using semantic caching to retrieve frequently-asked questions. In this chatbot example, users ask questions about internal source files like IRS filing documents, and get answers back 15X faster.
With context-aware data a top priority, semantic caching helps AI systems deliver not just faster, but more relevant responses. This is key for apps ranging from automated customer service to complex analytics in research.
Integrating semantic caching with LLMs
In apps with LLMs, vector search plays a crucial role in semantic caching frameworks. It lets LLMs sift through vast amounts of data fast, finding the most relevant information by comparing vectors for user queries and cached responses.
Benefits of semantic caching
Semantic caching delivers real advantages for LLM-powered apps. Here's what you get:
Faster responses
Cached responses return in milliseconds instead of the seconds it takes for an LLM to generate a fresh answer. For high-traffic apps, this difference is everything. Users get instant replies, and your system handles more concurrent requests without breaking a sweat.
Lower costs
LLM API calls add up fast. Every time you hit the cache instead of calling the model, you save money. Teams using semantic caching typically cut their LLM costs by 50% or more, depending on how repetitive their query patterns are. The more similar questions your users ask, the bigger the savings.
Better efficiency
Semantic caching reduces the computational load on your infrastructure. Instead of processing every query through the full LLM pipeline, your system handles repeat questions with a simple vector lookup. This frees up resources for the queries that actually need fresh responses.
Smarter matching
Traditional caching only works with exact matches. Semantic caching understands that "How do I reset my password?" and "I forgot my login credentials" are asking for the same information. This flexibility means your cache hit rate goes up dramatically, and users get relevant answers even when they phrase questions differently.
Use cases for semantic caching
Semantic caching works wherever you have LLMs handling similar queries repeatedly. Here are some of the most impactful use cases:
Customer support chatbots
Support teams field the same questions constantly: shipping times, return policies, account issues. Semantic caching lets your chatbot answer these instantly from cache, even when customers phrase them in unexpected ways. Response times drop from seconds to milliseconds, and your LLM costs shrink with every cached hit.
Internal knowledge bases
Enterprise apps that query internal docs, FAQs, or company policies benefit from semantic caching. Employees asking about HR policies, IT procedures, or project guidelines get fast answers without waiting for the LLM to regenerate the same information over and over.
E-commerce product search
When customers search for products, they often use different words for the same thing. Semantic caching recognizes that "running shoes," "jogging sneakers," and "athletic footwear" are similar queries and serves cached results instantly. This speeds up the shopping experience and reduces backend load during peak traffic.
Language translation apps
Translation apps handle a lot of repeated content: common phrases, standard greetings, frequently used sentences. Semantic caching stores these translations and serves them instantly when similar text comes through, cutting translation latency and improving accuracy by reusing verified results.
Content recommendation engines
Recommendation systems can use semantic caching to match user queries with previously served content. When users ask for similar types of recommendations, the system pulls from cache instead of recomputing suggestions, making the experience faster and more responsive.
Best practices for implementing semantic caching
Assessing your infrastructure
Effective implementation of semantic caching starts with choosing the right infrastructure. Some key considerations include:
- Data storage solutions – Opt for scalable storage solutions like Redis that can handle large volumes of data and support fast data retrieval. These systems are adept at managing the complex data structures necessary for semantic caching.
- Caching strategies – Decide between in-memory and persistent caching based on the application’s needs. In-memory caching offers faster access times but at a higher cost and with limitations on data volume. Persistent caching, while slower, can handle larger data sets and ensures data durability.
Designing for scalability & performance
To ensure that your semantic caching systems can handle increasing loads and maintain high performance, consider the following strategies:
- Load balancing – Implement load balancing to distribute queries effectively across the system, preventing any single part of the system from becoming a bottleneck.
- Data retrieval optimization – Use efficient algorithms for data retrieval that minimize latency. This includes optimizing the way data is indexed and queried in your vector and cache stores.
Ensuring accuracy & consistency
Maintaining accuracy and consistency in responses is essential, especially in dynamic environments where data and user interactions continuously evolve.
- Similarity thresholds – Manage similarity thresholds carefully to balance between response accuracy and the breadth of cached responses. Too tight a threshold may limit the usefulness of the cache while too loose a threshold might reduce the relevance of responses.
- Consistency strategies – Implement strategies to ensure that cached data remains consistent with the source data. This may involve regular updates and checks to align cached responses with current data and query trends.
Implementing semantic caching
To wrap these practices into a coherent implementation strategy, you can follow these steps:
- Step 1: Assess your current system’s capabilities and determine the need for scalability, response time, and cost improvement.
- Step 2: Choose appropriate caching and storage technologies that align with your system’s demands and budget.
- Step 3: Configure your semantic caching layer, focusing on key components like LLM wrappers, vector databases, and similarity searches.
- Step 4: Continuously monitor and adjust similarity thresholds and caching strategies to adapt to new data and changing user behavior patterns.
By following these best practices, organizations can harness the full potential of semantic caching, leading to enhanced performance, improved user experience, and greater operational efficiency.
A new era for apps
Semantic caching solves a real problem for LLM-powered apps: users ask the same questions in different ways, and traditional caching can't help. By matching queries based on meaning instead of exact strings, semantic caching cuts LLM API costs, speeds up response times, and improves the user experience.
Redis gives you everything you need for semantic caching in one place. As the world's fastest data platform, Redis combines sub-millisecond vector search with the caching and data structure support your apps already rely on. You don't need to stitch together separate vector databases, caches, and storage systems. Redis handles vectors, embeddings, and cached responses in a single product, so your architecture stays simple as your app scales.
Redis LangCache is our fully-managed semantic caching service, built to drop LLM costs and speed up responses without the infrastructure overhead. If you want to estimate your savings, check out the LangCache calculator. For a deeper look at caching strategies beyond semantic caching, we've got you covered there too.
Ready to get started? Try Redis free and see how fast your GenAI apps can be. Or if you want to talk through your architecture, meet with our team.
FAQs about semantic caching
Does semantic caching work with all LLMs?
Yes. Semantic caching works with any LLM, including OpenAI, Anthropic, Cohere, and open-source models. It sits between your app and the LLM API. The caching layer intercepts queries, checks for semantic matches in the cache, and only forwards cache misses to the LLM. This means you can implement semantic caching once and use it across multiple LLM providers without changing your caching logic.
Does semantic caching increase latency?
Semantic caching adds 5-20ms for the vector similarity search, but saves 1-5 seconds by skipping the LLM call. The net result is this: for cache hits, responses are typically 2-4x faster, with optimal cases reaching 50-100x faster. For cache misses, you pay the small vector search overhead plus the normal LLM latency.
Can I use semantic caching with streaming responses?
Yes. Semantic caching works with streaming responses through two approaches:
- Stream-then-cache: Stream the complete response to the user, then store it in the cache for subsequent queries. This provides cost savings for repeat queries but not for the initial request.
- Early-exit caching: For frequently-repeated queries, preload common responses in the cache before streaming begins. This allows instant cache hits for predictable questions while maintaining real-time streaming for novel queries.
Most production systems combine these and cache complete responses after streaming finishes while also preloading high-traffic queries to reduce first-request latency.
What happens when cached responses become outdated?
Set TTL (time-to-live) values based on how often your data changes:
- Rapidly changing data (prices, inventory): 5-15 minute TTLs
- Moderately changing data (product descriptions): 1-4 hour TTLs
- Stable data (FAQs, policies): 24-hour TTLs
You can also implement content-triggered cache invalidation. When you update source data, immediately flush related cache entries rather than waiting for TTL expiration. For example, if a product price updates, clear cache entries for that product. If a FAQ changes, invalidate related semantic matches.
How do I prevent semantic caching from serving wrong answers?
Start at a 0.90-0.95 threshold and monitor false positives. If they exceed 3-5%, threshold tuning alone won't fix it: you need architectural improvements. Log cached responses that users reject, and implement quality controls like preloading relevant cache entries or adding validation for malformed queries. Domain-specific embedding models also reduce false positives better than general-purpose ones.
Get started with Redis today
Speak to a Redis expert and learn more about enterprise-grade Redis today.
