Cluster Architecture
Redis Enterprise can be either a single Redis server database or a cluster. This allows a Redis Enterprise database to either scale horizontally across many servers through sharding or to copy data, which ensures high availability with Redis Enterprise replicas. Sharding is a type of database partitioning that separates large databases into smaller, faster, and more easily managed parts. These smaller parts are called data shards. With sharding or partitioning, you are not restricted to storing data on the memory of a single computer. Another advantage of sharding is being able to use the computational power of multiple cores.
In Redis Enterprise, a cluster is a set of cloud instances, virtual machine/container nodes, or bare-metal servers that let you create any number of Redis databases in a memory/storage pool that’s shared across the set. The cluster doesn’t need to scale up/out (or down/in) whenever a new database is created or deleted. A scaling operation is triggered only when one of the predefined limit thresholds has been reached, such as memory, CPU, network, and storage IOPS.
To create a sharded cluster, you need to first specify the number of shards. Once you’ve done this, your data will automatically be sharded or divided into groups and placed on optimal nodes.
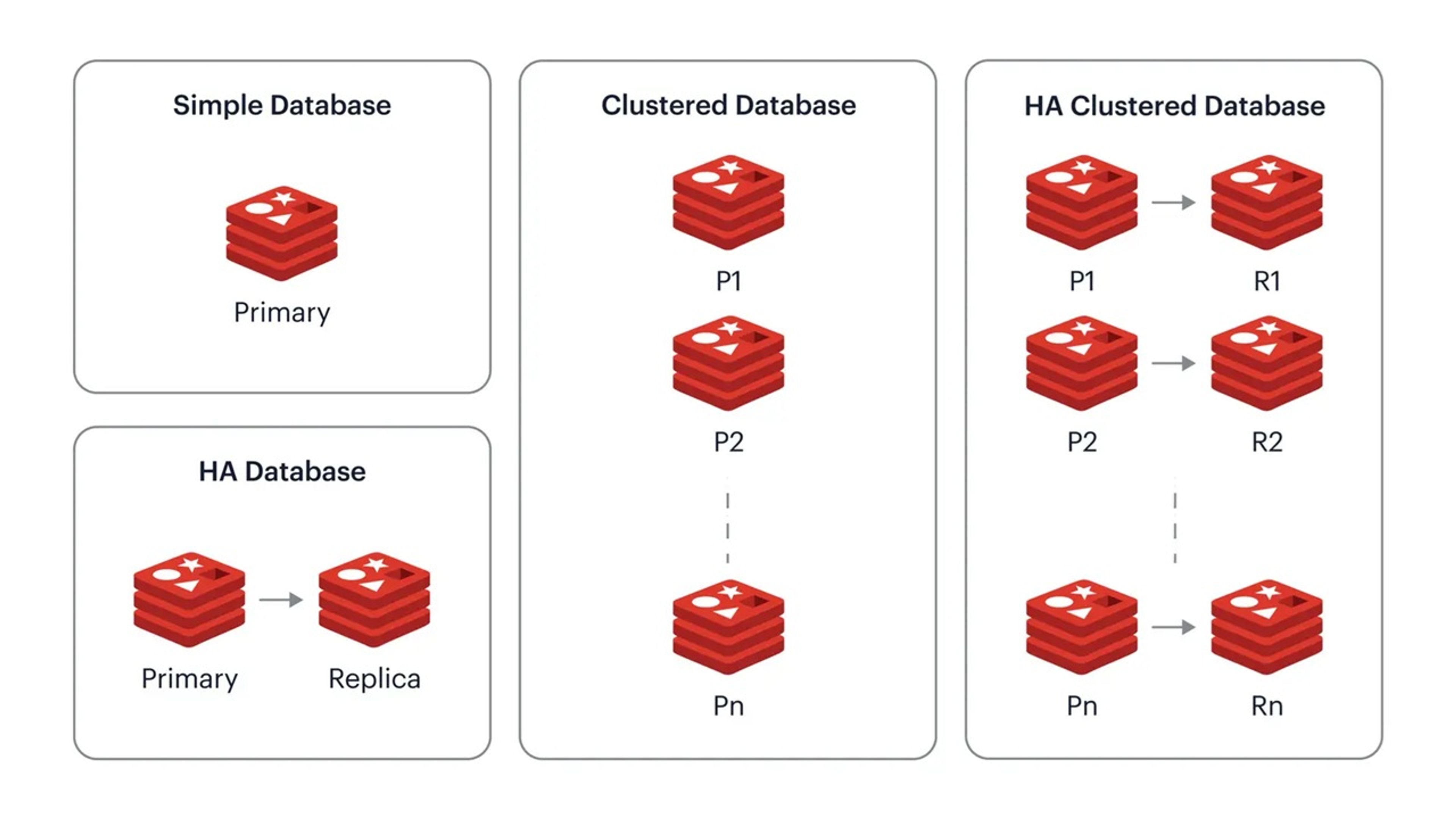
At any given time, a Redis Enterprise cluster node can include between zero and a few hundred Redis databases in one of the following types:
- A simple database, i.e. a single primary shard
- A highly available (HA) database, i.e. a pair of primary and replica shards
- A clustered database, which contains multiple primary shards, each managing a subset of the dataset (or in Redis terms, a different range of “hash-slots”)
- An HA clustered database, i.e. multiple pairs of primary/replica shards
Each database can be built in several forms:
- A Redis on DRAM database
- A Redis on Flash database, in which Flash (SSD or persistent memory) is used as a DRAM extender
Each database can be accessed in multiple ways:
- Database endpoint: Simply connect your application to your database endpoint (a unique URL and port on the fully qualified domain name), and Redis Enterprise will transparently handle all the scaling and failover operations.
- Sentinel API: Use sentinel protocol to connect to the correct node in the cluster in order to access your database.
- OSS Cluster API: Use the cluster API to directly connect to each shard of your cluster without any additional hops.
Multiple databases from different applications and users can run on the same Redis Enterprise cluster and node while fully isolated with multi-tenancy.
High availability
Planning for disaster recovery and zero downtime means having a replica set of the Redis Enterprise cluster across a single region or several regions. High availability clusters are a group of hosts that merge as a single system to prevent downtime.
If one server in a high availability cluster goes down, the mission-critical application is immediately transferred to another server as soon as the fault is detected. Redis Enterprise will ensure that the replica shard process is always created on a different node to achieve high failover. If nodes go down, Redis Enterprise will make sure that the replica shard process on the other available node becomes the new primary shard.
A high availability cluster will utilize multiple systems and multiple primary and replica nodes that are already integrated. So should a failure cause one system to fail, another can be efficiently leveraged to maintain the continuity of the service or application being used.
Shared-nothing, linearly scalable, multi-tenant, symmetric architecture
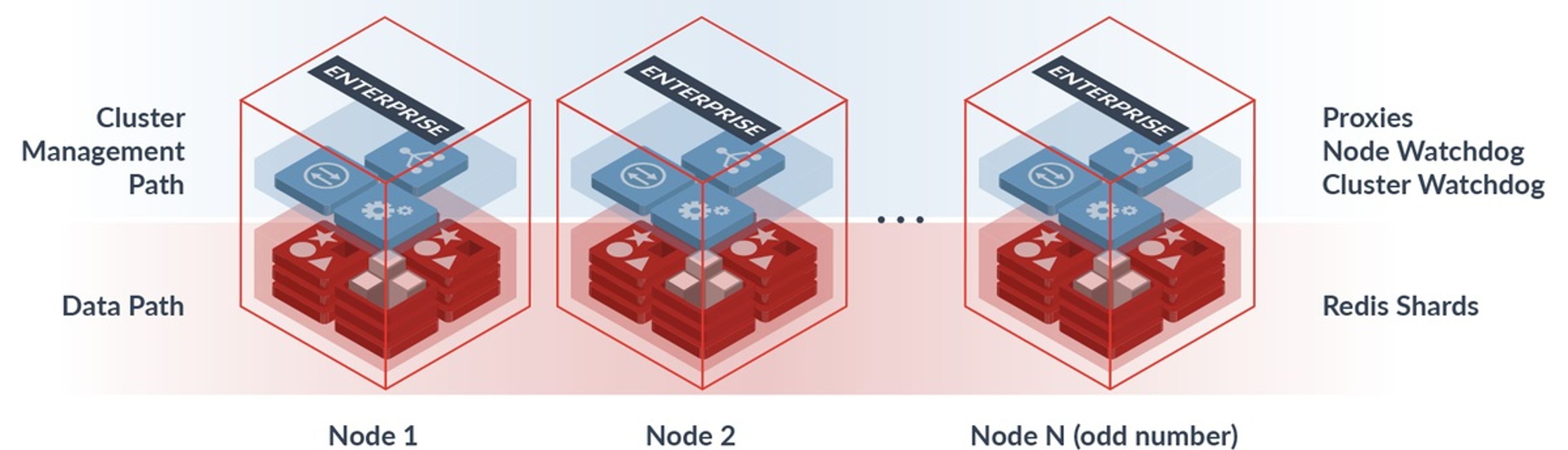
Redis Enterprise cluster is built on a complete separation between the data-path components (i.e proxies and shards) and the control/management path components (i.e. cluster-management processes), which provides a number of significant benefits:
- Performance: Data-path entities need not deal with control and management duties. The Redis Enterprise architecture guarantees that any processing cycles are dedicated to serving users’ requests, which improves the overall performance. For example, each Redis shard in a Redis Enterprise cluster works as if it were a standalone Redis instance. The shard doesn’t need to monitor other Redis instances, has no need to deal with failure or partition events, and is unaware of which hash-slots are being managed.
- Availability: The application continues to access data from its Redis database, even as sharding, re-sharding, and re-balancing takes place. No manual changes are needed to ensure data access.
- Security: Redis Enterprise prevents configuration commands from being executed via the regular Redis APIs. Any configuration operation is allowed through a secure Redis CLI, UI, or API interface that follows role-based authorization controls. The proxy-based architecture ensures that only certified connections can be created with each shard and Redis shards can receive only certified requests.
- Manageability: Database provisioning, configuration changes, software updates, and more are done with a single command (via UI or API) in a distributed manner and without interrupting user traffic.
- Scalability: Databases scale horizontally by distributing data sets across multiple nodes, servers, and clusters. Scaling involves robust replication of partitioned database instances to multiple nodes.
Cluster components
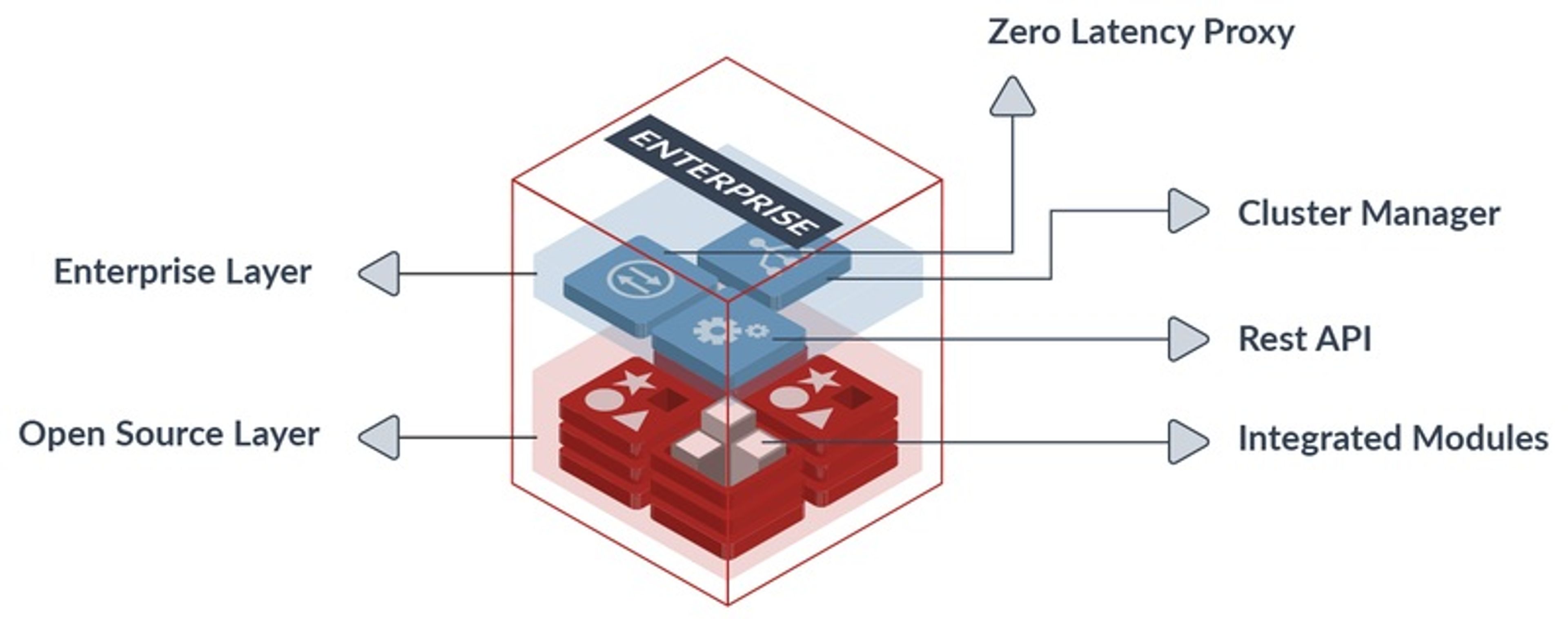
Redis Enterprise cluster is built on a symmetric architecture, with all nodes containing the following components:
- Redis shard: An open source Redis cluster or open source Redis instance with either a primary or replica role that is part of the database.
- Zero-latency proxy: The proxy runs on each node of the cluster, is written in C, and based on a cut-through, multi-threaded, lock-free stateless architecture. The proxy handles the following primary functionalities:
- Hides cluster complexity from the application/user
- Maintains the database endpoint
- Requests forwarding
- Manages data encryption through SSL
- Provides strong, client-based SSL authentication
- Enables Redis acceleration through pipelining and connection management
- Cluster manager: This component contains a set of distributed processes that together manage the entire cluster lifecycle. The cluster manager entity is completely separated from the data path components (proxies and Redis shards) and has the following responsibilities:
- database provisioning and de-provisioning
- Database provisioning and de-provisioning for optimal resource utilization
- Automatically scaling to handle peak workloads
- Automatically re-sharding to guarantee high-throughput, low latency, real-time performance
- Automatically re-balancing to guarantee high-throughput, low latency, real-time performance
- Resource management monitoring the entire system’s health
- Node watchdog that monitors all processes running on a given Redis node and triggers a shard failure event
- Cluster watchdog that is responsible for the health of the Redis cluster nodes and triggers a node failure event
- Secure REST API: In cluster mode, all the management and control operations on Redis Enterprise are performed through a dedicated and secure API that is resistant to attacks and provides better control of cluster admin operations. One of the main advantages of this interface is the ability to provision and de-provision Redis resources at a very high rate, with almost no dependency on the underlying infrastructure. This makes it very suitable for microservices-based architectures.
To optimize resources in a Redis Enterprise cluster, you should:
- Adopt platforms that scale to thousands of database instances in support of high-volume concurrency across disparate workloads
- Use multi-tenancy to allow multiple database endpoints to run in a single cluster, thereby maximizing infrastructure utilization, enabling endpoint-level database optimization, avoiding performance degradation, and safeguarding database security
- Use intelligent storage tiering so that frequently used “hot” data stays in memory while less-frequently used “cold” data goes on flash, SSD, rotating storage, or tape, with the system automatically balancing and otherwise managing where data is physically persisted
- Run test, development, and production databases on separate tenants, nodes, or clusters, providing workload isolation and enabling independent provisioning, management, and optimization to meet their various scaling, performance, and availability requirements
FAQs
To start the Redis client, open the terminal and type the command redis-cli. This will connect to your local server, and now you can run any command. In the above example, we connect to the Redis server running on the local machine and execute a command PING that checks whether the server is running.
Linear scalability means that the amount of resources increases at the same proportion as your database throughput and in a deterministic manner. For example, increasing your cluster resources by 50% will translate to 50% throughput increases. Redis Enterprise supports the open source cluster API, enabling infinite, linear scaling by simply adding shards and nodes.
Redis Enterprise Software offers uninterrupted high availability with five-nines (99.999%) uptime. By using technologies like diskless replication, instant failure detection, and single-digit-second failover across racks, zones, and geographies, Redis Enterprise delivers high availability while being more cost-effective than competing technologies. Redis Enterprise Software automates cluster management to provide confidence that the Redis cluster and Redis clients will always be available. Redis Enterprise Software offers several ways to ensure data consistency and reliability, including active-active data replication, AoF (append on file) persistence, and snapshots.
Redis Labs was rebranded Redis in 2021. We rebranded to emphasize that Redis Ltd (the company) is responsible for source available Redis and Redis Enterprise. As the official sponsor of open source Redis, Redis understands how important it is to the developer community and is committed to ensuring open source Redis is always freely available. Redis is also developing the market’s most scalable, reliable, and highly available in-memory real-time data platform, Redis Enterprise Software, and Redis Cloud.
Get started with Redis today
Speak to a Redis expert and learn more about enterprise-grade Redis today.