Blog
Search Benchmarking: RediSearch vs. Elasticsearch
Click to learn more about RediSearch: RediSearch: A High Performance Search Engine as a Redis Module white paper
Background
RediSearch is a distributed full-text search and aggregation engine built as a module on top of Redis. It enables users to execute complex search queries on their Redis dataset in an extremely fast manner. The unique architecture of RediSearch, which was written in C and built from the ground up on optimized data structures, makes it a true alternative to other search engines in the market. It works great as a standalone search engine for indexing and for retrieval of searchable data.
When we first launched RediSearch, we benchmarked it against popular search engines like Elasticsearch and Solr to test how powerful the engine is. This time, we decided to try a slightly different benchmark in order to (a) give you a clear, reproducible setup, with all search engines optimized to provide their best performance and (b) simulate multiple real life scenarios based on what we see from our RediSearch users.
The Benchmark
In this Search benchmark, we compared RediSearch to Elasticsearch over two use cases:
- Index and query the wikipedia dataset
- Fast indexing in a multi-tenant environment
Wikipedia benchmark
We first indexed 5.6 million docs (5.3GB) from Wikipedia and then performed two-word search queries over the indexed dataset.
Indexing results
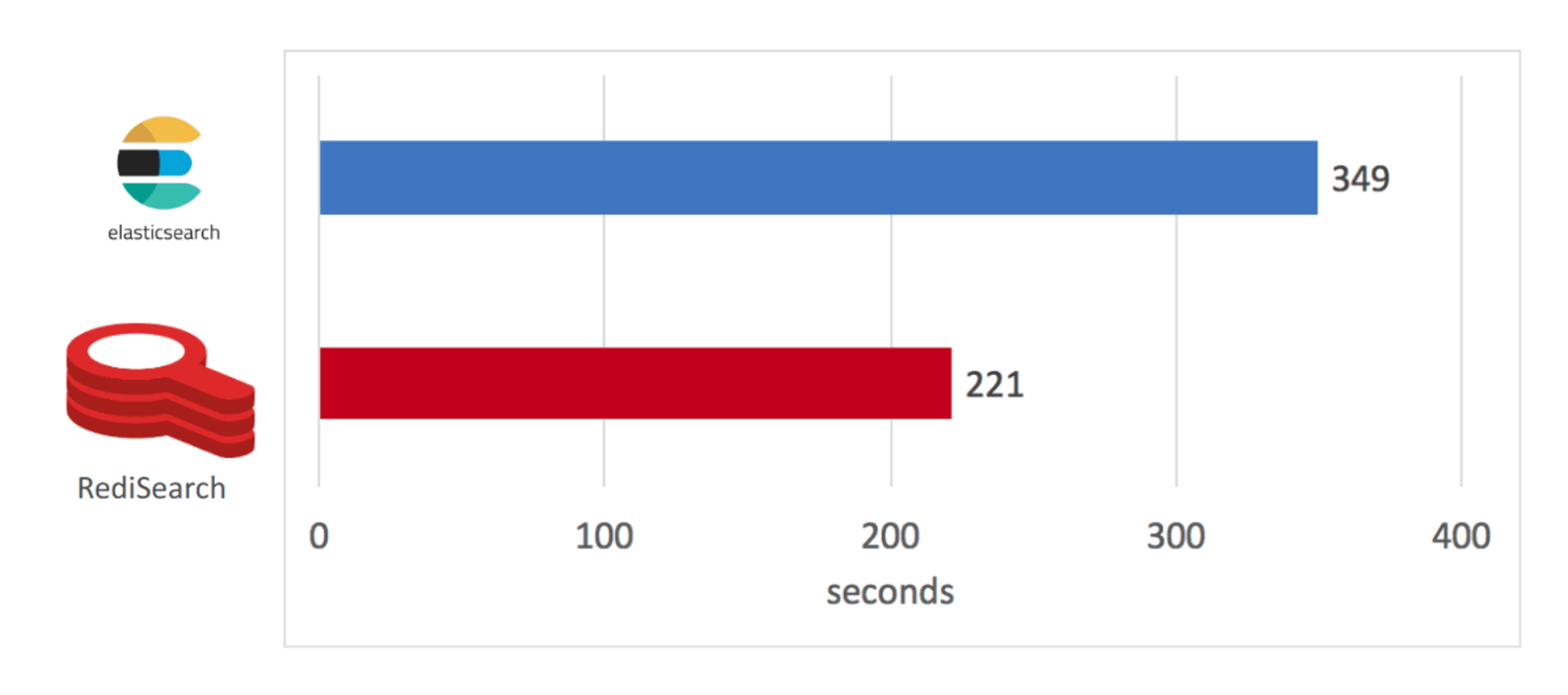
As you can see in the figure below, RediSearch built its index in 221 seconds versus 349 seconds for Elasticsearch, or 58% faster.
Querying results
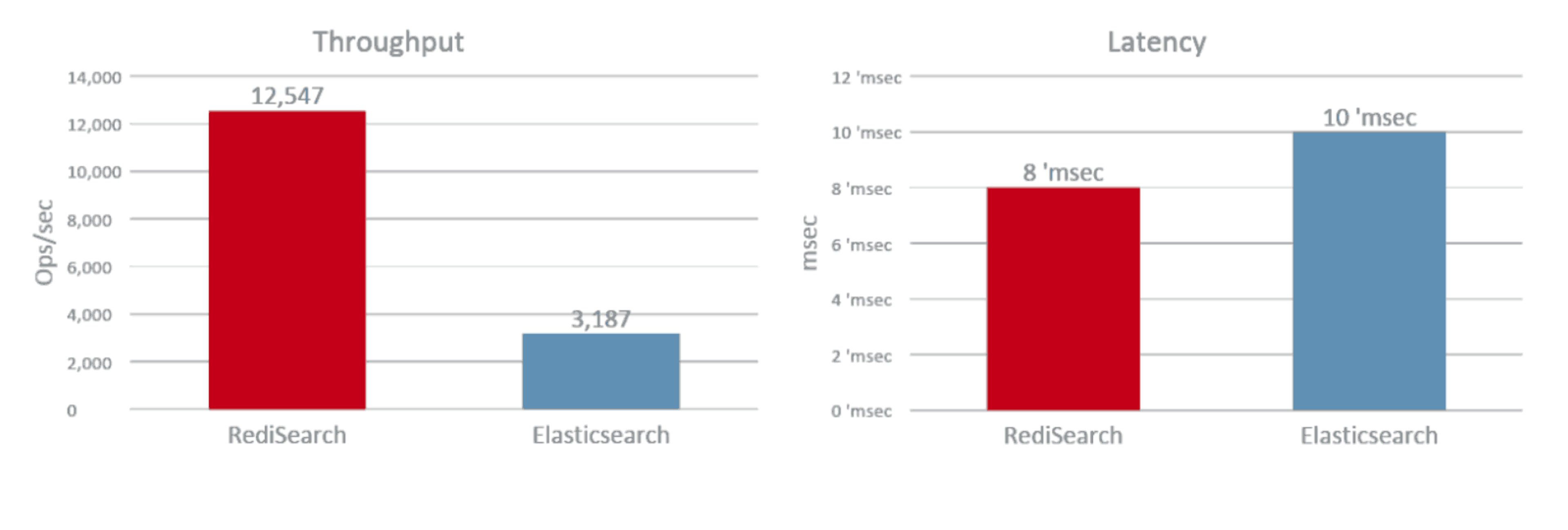
Once the dataset was indexed, we launched two-word search queries using 32 clients running on a dedicated load-generator server. As you can see in the figure below, RediSearch throughput reached 12.5K ops/sec compared to 3.1K ops/sec with Elasticsearch, or x4 faster. Furthermore, RediSearch latency was slightly better, at 8msec on average compared to 10msec with Elasticsearch.
Multi-tenant indexing benchmark
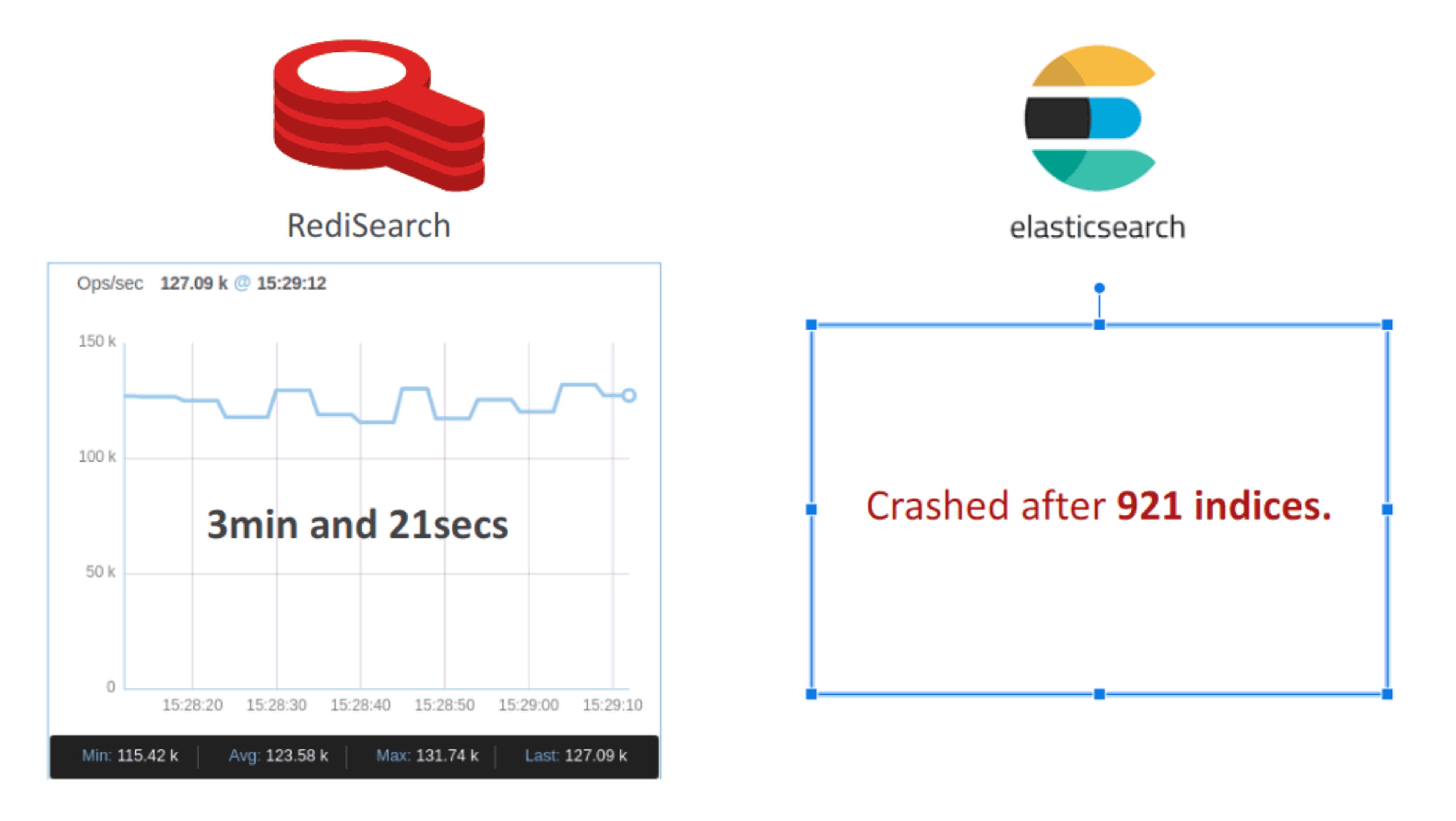
Here, we simulated a multi-tenant e-commerce application where each tenant represented a product category and maintained its own index. For this benchmark, we built 50K indices (or products), which each stored up to 500 documents (or items), for a total of 25 million docs. RediSearch built the indices in just 201 seconds, while running an average of 125K indices/sec. However, Elasticsearch crashed after 921 indices and clearly was not designed to cope with this load.
Benchmark setup
Hardware
| One AWS c4.8xlarge: One for the load-generator and one for the search engine | 36 | 60 | 10 Gigabit |
|---|
Dataset source
| wikidump | Date: Feb 7, 2019 | 5.6M | 5.3 GB |
|---|
RediSearch configuration
| Number of shards | 5 for the Wikipedia benchmark 20 for the multi-tenant benchmark |
|---|---|
| Doc table size | 10M |
Elasticsearch configuration
| Number of shards | 5 |
|---|---|
| JVM settings (Xms and Xmx) | 25GB |
| index.refresh_interval | -1 |
| index.number_of_replicas | 0 |
| Indices.queries.cache.size and index.queries.cache.enabled | Like mentioned here |
Versions
| RediSearch | Version 1.4.3 |
|---|---|
| Elasticsearch | Version 6.6.0 with Lucene version 7.6.0 |
| RediSearchBenchmark | Benchmark code here |
Conclusion
We benchmarked RediSearch and Elasticsearch for the following use cases:
- A simple Wikipedia use case – We found RediSearch faster by 58% on indexing and x4 faster when performing two-word searches on the indexed dataset.
- A more advanced multi-tenant use case – RediSearch created 50k indices in just 201 seconds while Elasticsearch crashed after 921 indices were created.
Elasticsearch is a great feature-rich search product created by the great people at Elastic.co, but when it comes to performance, it has inherent architecture deficiencies, as summarized by the table below:
| Search engine | Dedicated engine based on modern and optimized data-structures | based on Lucene engine |
|---|---|---|
| Programming language | C-based, extremely optimized | Java |
| Memory technology | Runs natively on DRAM and Persistent Memory | Disk-based with a caching option |
| Protocol | The optimized RESP (REdis Serialization Protocol) | HTTP |
Read more about RediSearch here and the technology behind it. To get started with RediSearch – try our Redis Cloud Pro here or download Redis Enterprise Software here.
Appendix
Following feedback from readers we updated the reference to the wikipedia dataset and added a link to the benchmark source code for reproduction purposes. We would be happy to get more feedback if any.
Get started with Redis today
Speak to a Redis expert and learn more about enterprise-grade Redis today.
