Blog
Introducing Redis Data Integration
Redis is announcing the public preview release of Redis Data Integration (RDI). RDI lets developers offload a database to Redis Enterprise, mirror application data, and operate at in-memory speeds. And you don’t need to invest in coding or integration efforts.
The underlying problem: Your existing database is too slow.
You have a lot of applications, a growing number of users, increasing technical demands, and an unrelenting demand for real-time response. Redis Enterprise provides real-time access to data and it scales horizontally, but how do you keep your Redis cache in line with your database so that all queries can be executed from the cache?
Some organizations decide to take it on themselves – only to discover how hard it is to build a cache prefetch (or refresh ahead, as it is sometimes called). To create one, you need to build a reliable streaming pipeline. That starts with capturing all data changes in the source database as they occur, and then translating the data to Redis data types to allow an application to fetch it. This process typically involves data transformations and denormalizations.
We saw users struggling to build these streaming pipelines on their own. It required integration of several components (Change Data Capture (CDC), streaming, and Redis connectors), coding transformations, error handling, and many other enterprise essential requirements. That tool-building time could be spent on more productive endeavors that the business is waiting for.
We decided to take on the challenge ourselves.
Enter Redis Data Integration
Redis Data Integration (RDI) is a tool that runs inside Redis Enterprise. It helps you synchronize data from your existing relational database into Redis in near real-time so thatapplication read queries are completely offloaded from the relational database to Redis.
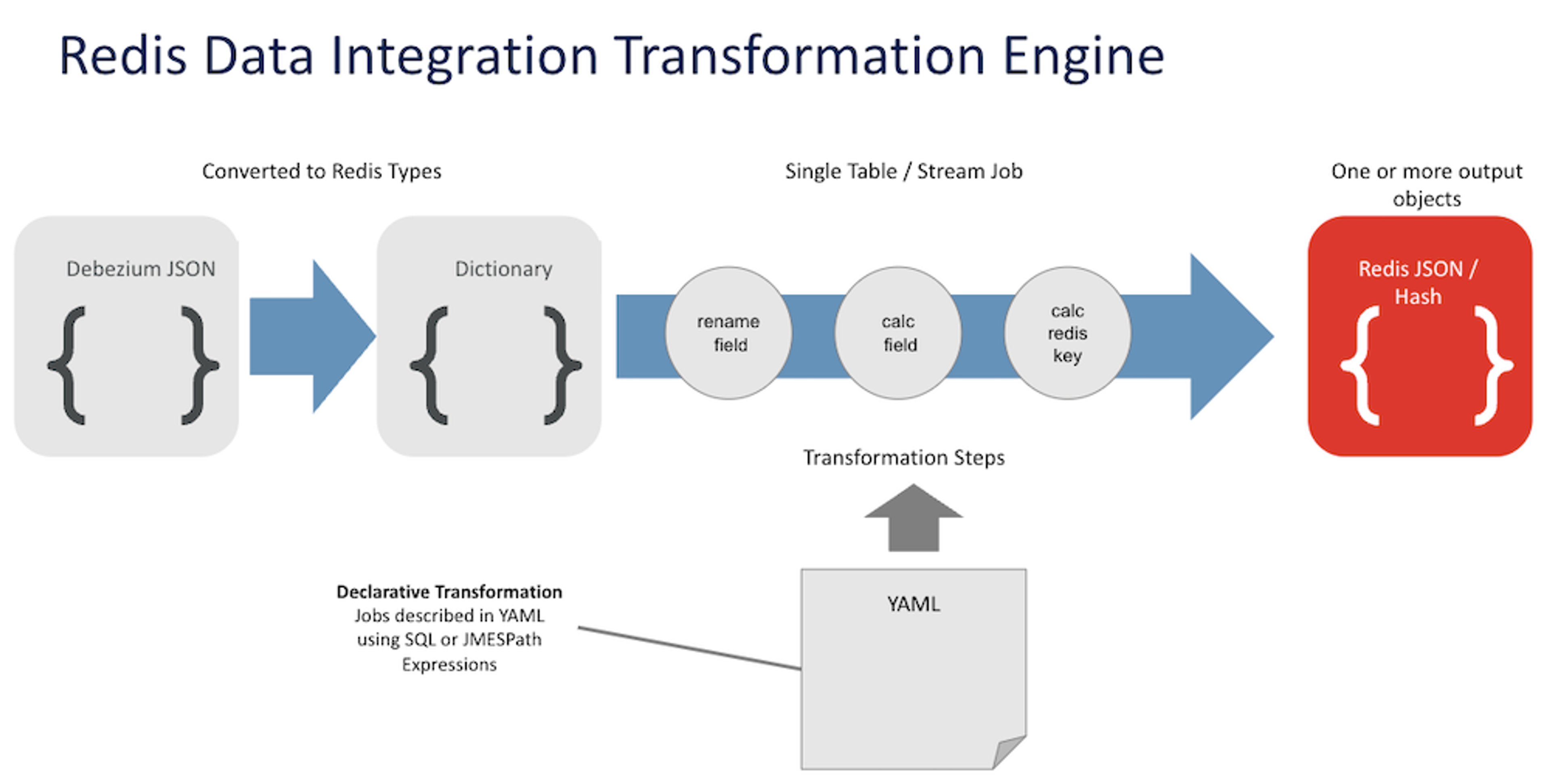
The data transformation process
RDI pipelines have two stages:
- Capturing the database changes and streaming them into RDI transformation jobs
- Transforming and denormalizing the data using declarative instructions and then writing it to the target Redis cache
The data transformation process
Debezium, an open-source CDC platform, captures changes to data in the source database and streams it into RDI. Within Redis, the data may be further filtered, transformed, and mapped to one or more Redis keys. RDI supports several Redis data types (Hash, JSON, Set, and Stream). RDI writes the data to the destination Redis database.
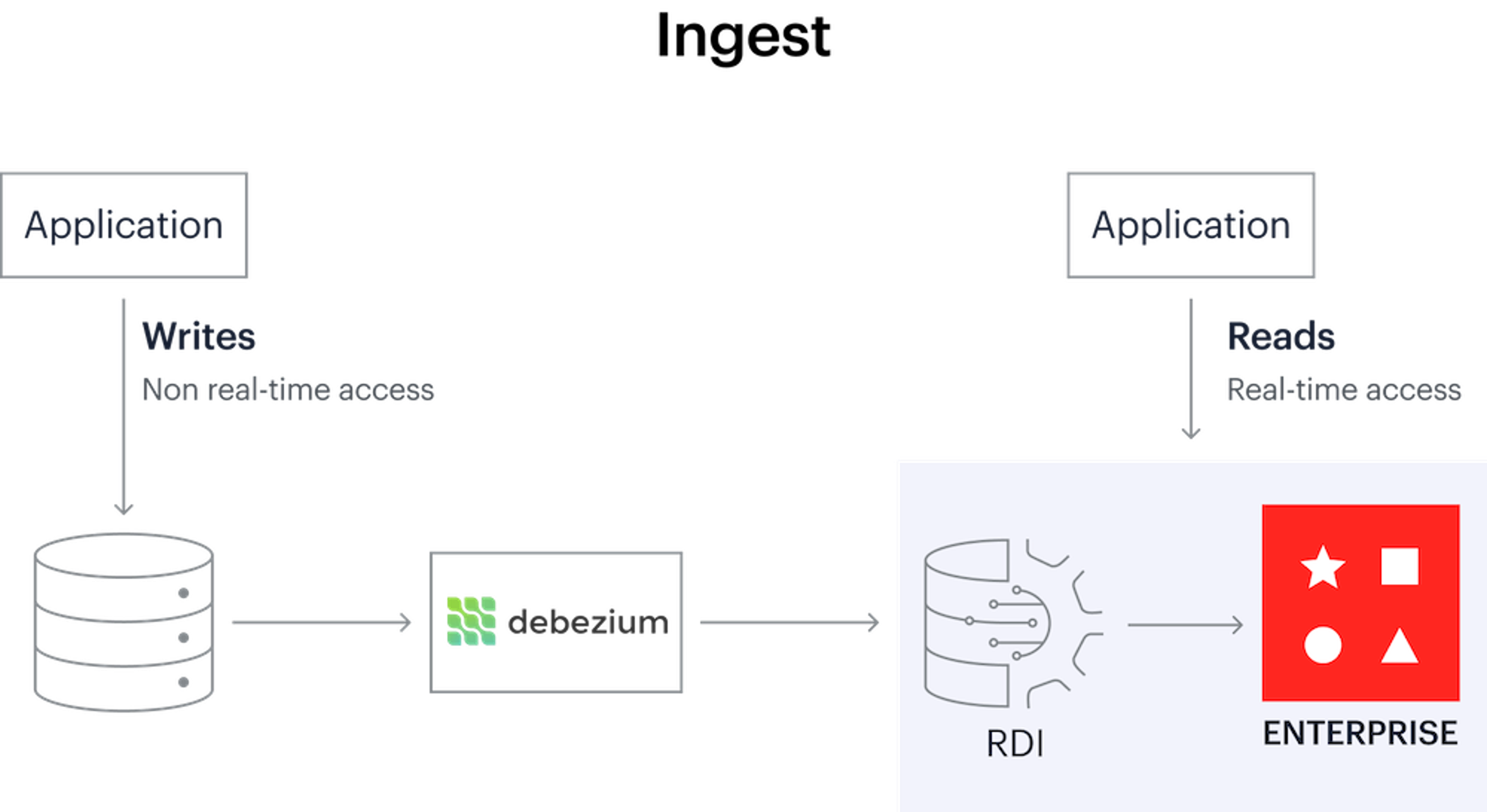
Ingest with the Debezium server
It does the heavy lifting, so developers can focus on application code instead of on integration chores and data transformation code.
RDI can connect with other CDC tools and streaming data. We already started building our ecosystem, and are happy to share that we have a technology partnership with Arcion.
With this integrated solution, developers have a simple way to stream changes from a variety of databases to Redis Enterprise and other data platforms, using RDI as the backbone.
Codeless data filtering and transformations
Capturing changes from a source database and getting the data from one place to another is difficult enough. However, there is yet another challenge in moving data: the transformation part, which means filtering data and mapping the data to Redis data models.
RDI provides an option to specify all the filtering and transformation steps required per source table. This is called a job, in RDI terms; every job is a YAML file.
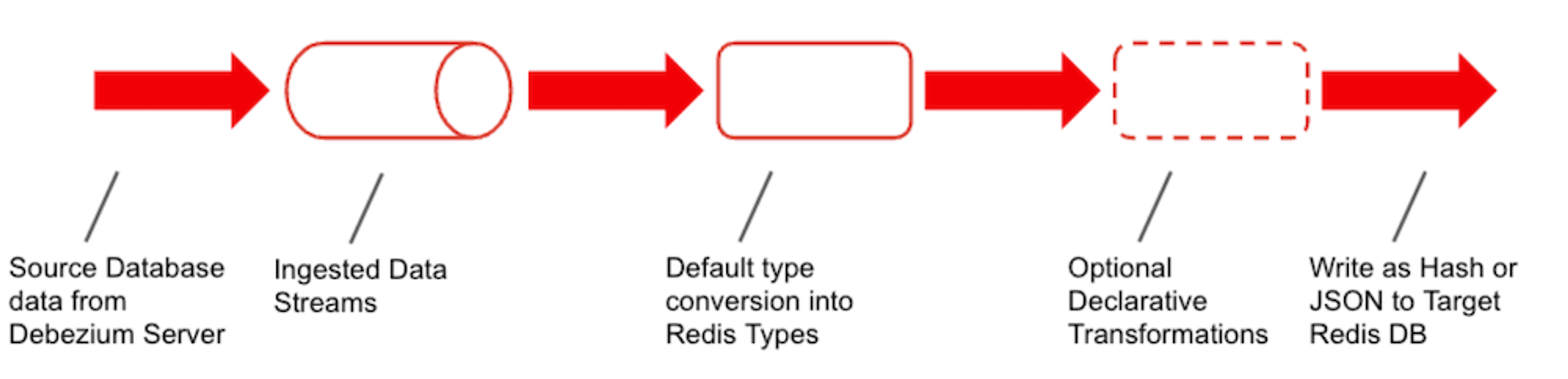
Data transformation pipeline
Filtering is important. CDC products provide complex filtering, but you have to write custom code. RDI does the same without coding. Instead, a declarative filter using SQL expressions or Jmespath functions is applied. RDI comes with additional custom Jmespath functions for the convenience of the job creator.
RDI has several levels of data transformation:
- Basic transformation: This is done automatically by the RDI engine.
- Structuring: The RDI engine has a default way to structure as Hash or JSON with the power of codeless transformation. You have options to transform keys and fields, even to recalculate values in those fields.
- Denormalization: RDI translates the source to a JSON document where parent details from the document gets translated into a map of JSON objects.
RDI includes a Trace tool that helps you create and troubleshoot complex data pipelines without writing custom code. That speeds up the process and reduces the required efforts and skill set.
After troubleshooting, amending the pipeline is done by a simple deploy command with no downtime.
Additional features in the public preview:
- At least once delivery guaranteed
- High Availability of Debezium Server and RDI
- Hard rejected entries handling in Dead Letter Queue (DLQ)
- Source databases supported: Oracle, Postgres, MySQL, MariaDB, Percona XtraDB, Microsoft SQL Server, and Cassandra (Including DataStax DSE)
- Data extraction modes: Initial snapshot and CDC (Stream changes)
- Declarative transformations: filter condition, Redis key pattern, change field names, add field, remove field, nest
- Supported Redis data types: Hash, JSON, Set, Stream
- Developer tools: RDI command-line interface scaffold and trace commands
- Operator tools: RDI command-line interface, Grafana dashboard (metrics via Prometheus exporter)
Learn more in our Redis Data Integration documentation.
Is RDI right for you?
RDI is ideally suited for applications that meet the following criteria:
- Application data is coming from a relational database that can not be replaced
- The relational database can accommodate the pace of data writes but can not scale and perform to serve the load of read queries. It is essential to offload read queries from the relational database.
- It is critical that the data in the cache reflects the data in the relational database in near real time.
- A relational database with a moderate to high change rate where a batch process to insert changes does not satisfy the requirements.
- Data mapping between the source database and Redis requires some data manipulations.
Looking ahead
This is a public preview. We are seeing RDI Ingest flow to general availability, we are working on features to integrate Redis in the opposite direction: to apply changes to Redis data to downstream databases.
- Write-behind: The CDC source is your Redis database and your target is a downstream relational or NoSQL database. This flow will allow you to enjoy Redis Enterprise’s real-time speed for both writes and reads while retaining your application ecosystem and downstream services.
- Write-through: Each write to Redis is also applied to the database.
- Read-through: In case of a cache miss, RDI automatically fetches the missing data from a downstream database and writes it back as a key to Redis so it can be returned to the requesting application.
Get started with RDI
RDI is currently available only for self-managed Redis Enterprise clusters.
If you are an existing customer of Redis Enterprise, download the RDI CLI package and follow the steps in the quick start guide. The installation guide walks you through installing and configuring the Debezium server. After you run a handful of RDI CLI commands, your pipeline will begin moving data from your source database to Redis.
If you are not an existing customer of Redis Enterprise, you need to first install Redis Enterprise Software for Kubernetes. Then download the RDI CLI package and follow the steps in the quick start guide.
Get started with Redis today
Speak to a Redis expert and learn more about enterprise-grade Redis today.
