Blog
Serverless Development with AWS Lambda and Redis Enterprise Cloud
In this blog post, you will learn how to integrate AWS Lambda and Redis Enterprise Cloud. Using a sample movie-database application, you will discover how to build and deploy two Lambda functions, one in Node.js, one in Python. These two Lambda functions are used to interact with the Redis database to insert, update, delete, and query. The application uses the RediSearch API that provides rich query and search functionalities. Serverless, using AWS Lambda, fits into the growing trend towards microservice architectures as it allows developers to reduce the scope of a business “service” into a small project that can be implemented using the programming language of their choice. To learn more, watch the video below and read on for a quick overview of AWS Lambda and a deeper dive into how to build an application using Redis Enterprise Cloud and Lambda:
A quick look at AWS Lambda
If you’re not already familiar with AWS Lambda—the company’s serverless compute runtime, also known as a Function-as-a-Service (FaaS)—here are the basics you need to know. (Lambda experts can jump ahead to the next section.) AWS Lambda allows applications to run a function on demand in response to a particular event, making it a good way to build event-driven architecture (EDA) applications. AWS Lambda functions, fully managed by AWS, can be created using various programming languages. Perhaps the best part of AWS Lambda is that developers don’t usually need to fully understand the application lifecycle to use it.
AWS Lambda can be invoked using several different methods: directly from the AWS Console, using events from other AWS Services such as SNS, SQS, or Kinesis, or even from the AWS Console, CloudWatch, or S3 events. In our sample movie-database application, the Lambda functions will be invoked using an HTTP REST endpoint, this is done using the AWS API Gateway. (You can find more about AWS Lambda function invocation in the documentation.)
AWS Lambda HTTP execution process
Specifically, requests via HTTP are routed to AWS’ API Gateway management tool, which parses the body, header, and parameters, and then triggers our Lambda function with this payload:
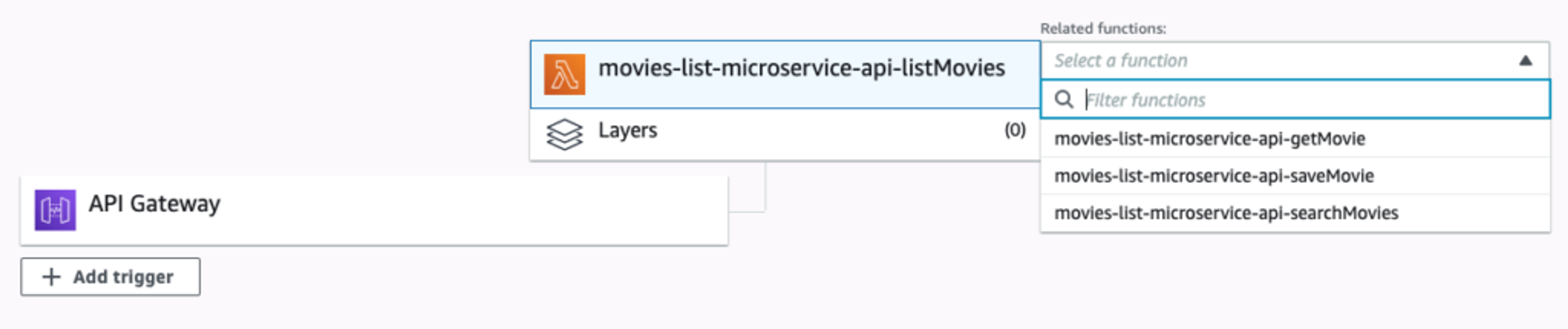
Exposing a AWS Lambda function in the API Gateway.
As a developer, you simply write code to expose the REST endpoint and configure the deployment to expose it inside the AWS API Gateway. (We’ll discuss this further in the next section covering our sample movie-database application.)
State and data management in serverless applications
AWS Lambda is a stateless environment. In many applications, though, you still want to share state between services or calls, and Redis can help. For simple state management, AWS developers often use ElastiCache, but many applications require more than state management, they also need persistence, rich data, high performance, and a query model. Redis Enterprise Cloud provides a fully managed service on AWS (Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure are also supported).
Redis movie-database sample application
Now we’re ready to look at our sample movie-database application to see the key steps to build an application using Redis Enterprise Cloud and AWS Lambda.
The application uses the dataset that has been documented in the RediSearch Getting Started tutorial, which consists of a movie catalog, made of Redis Hashes. As shown in the chart below, the frontend is built using Vue.js, which calls REST endpoints to:
- List, sort, and filter movies
- Edit movies and add/delete comments
- Search movies using full-text search and faceted search
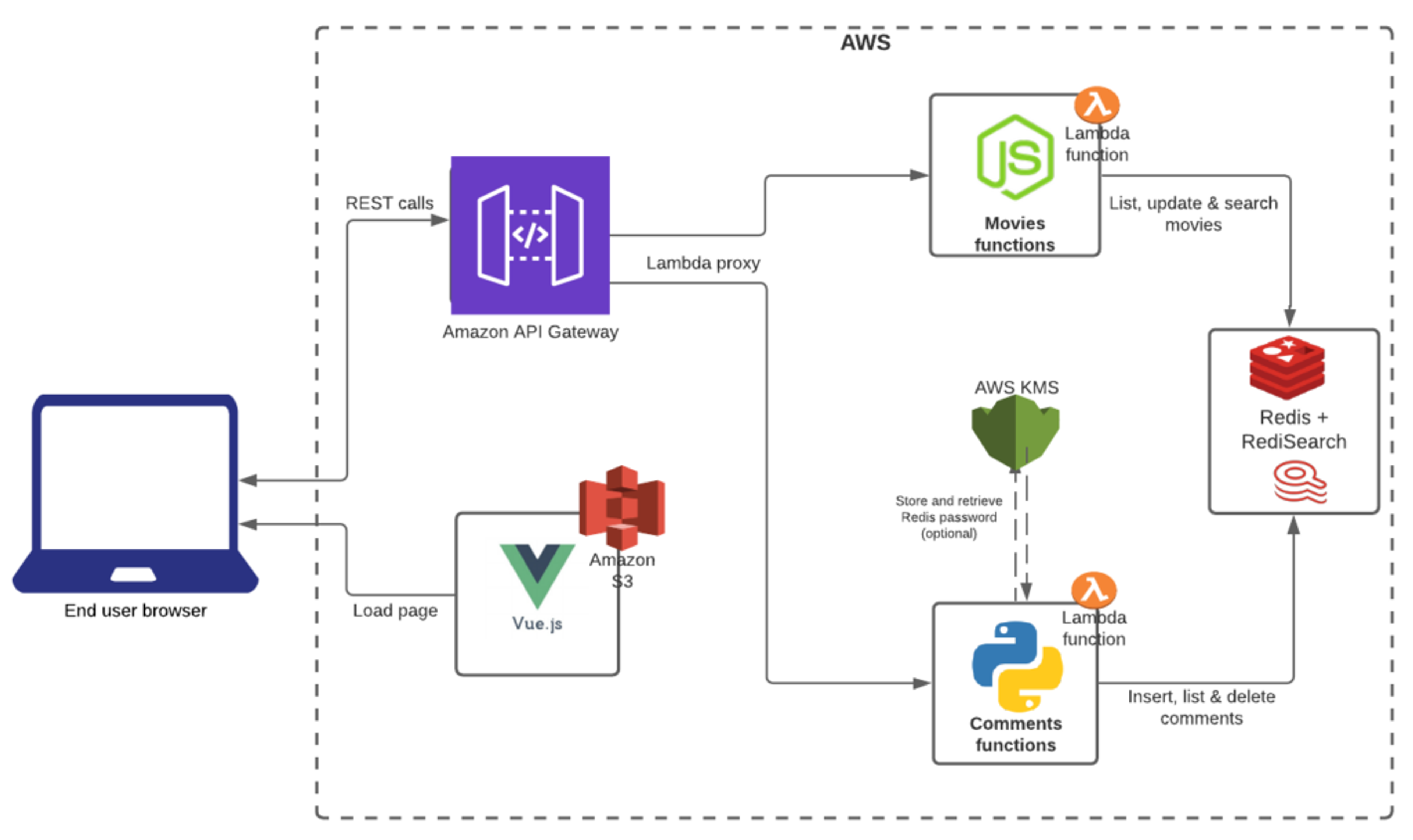
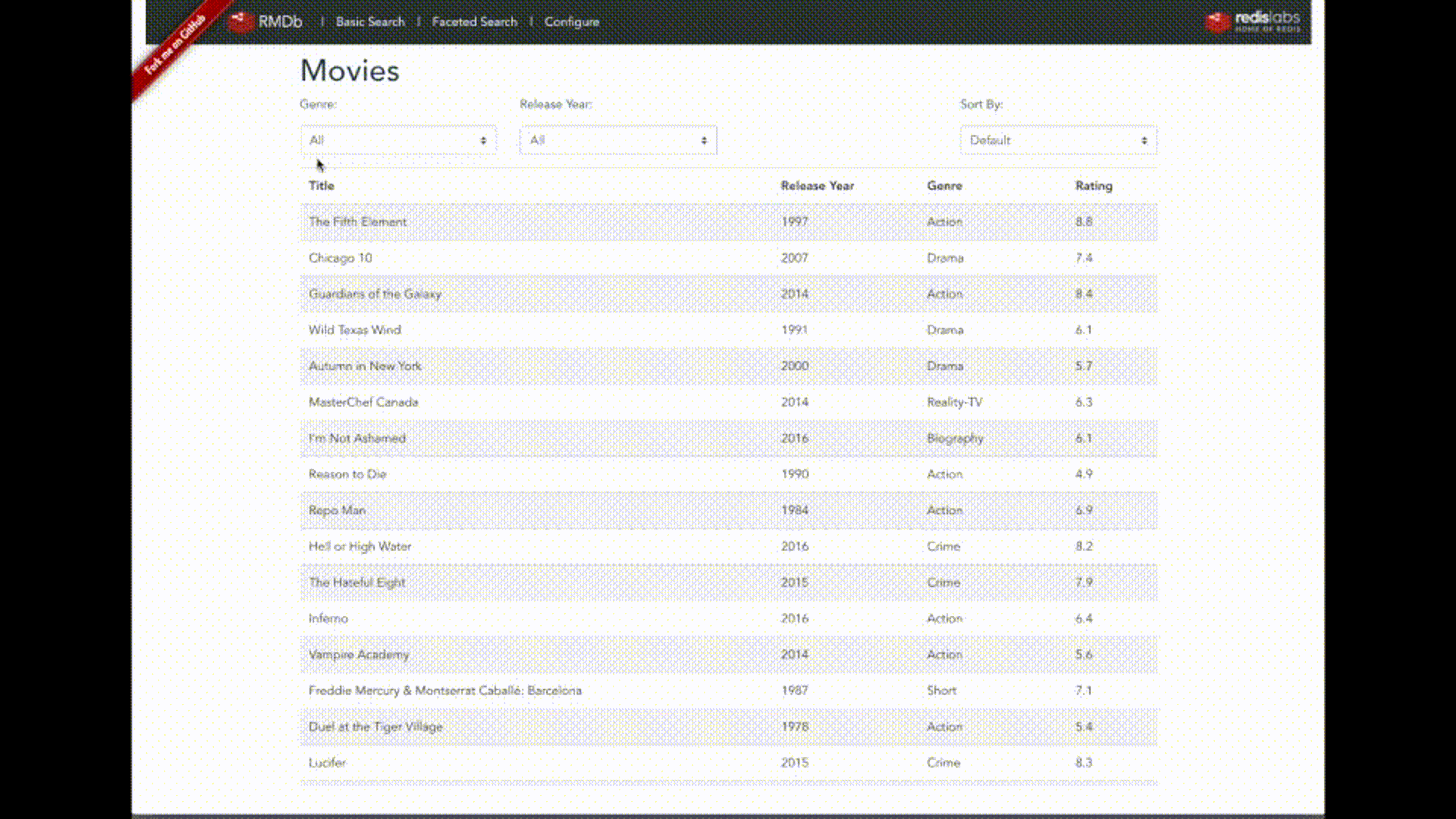
A demo of the sample movie-database application using AWS Lambda functions.
As mentioned above, the application leverages the AWS API Gateway, AWS Lambda, and Redis Enterprise Cloud for the datastore. In addition, the Python service uses AWS Key Management Service to store and encrypt the Redis database password.
Install and run the demonstration application
To get started, you’ll need a few prerequisites:
- An AWS account setup, credentials, with the CLI Installed
- A Redis Enterprise Cloud account and database, with the RediSearch module enabled
- Git
- Node.js
- Python
- The Redis command line interface (CLI)
Once you have everything assembled, let’s walk through the process of installing and running the sample application.
Step 1: Get the Redis Enterprise Cloud database information
If you have not yet created a database on Redis Enterprise Cloud, please do so using the information in our Get Started with Redis Modules guide.
When you are connected to the Redis Enterprise Cloud, you can find the database connection information in the web console; be sure you add the module “RediSearch 2” to the database.
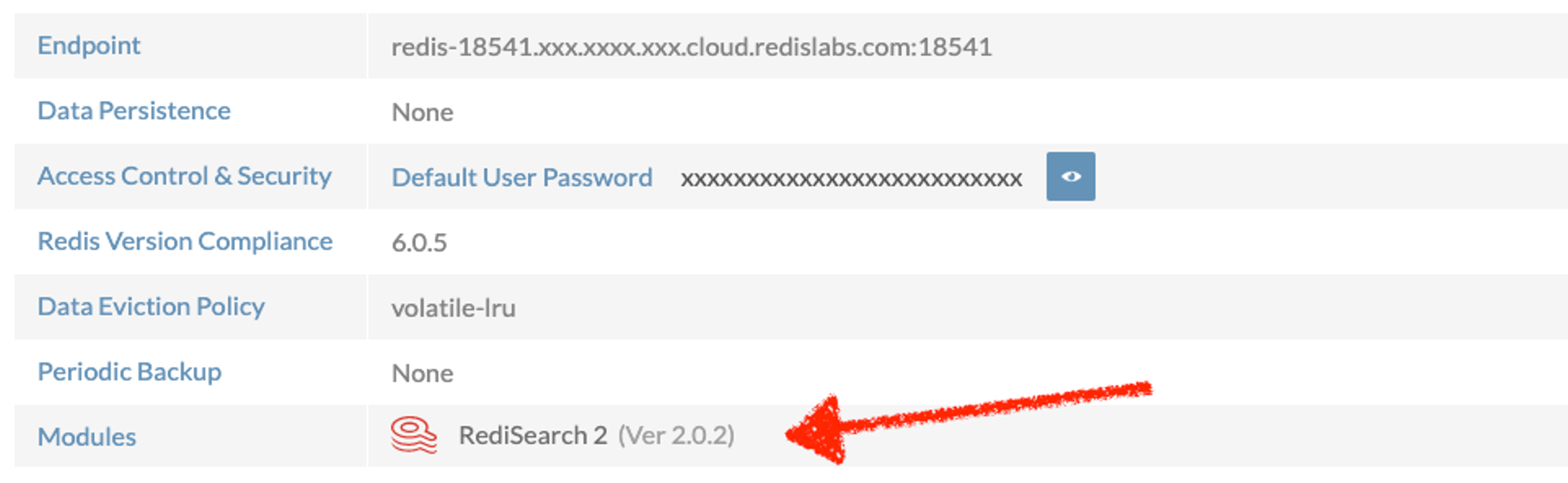
Redis Enterprise Cloud database information for our sample movie-database application.
You will need the following properties to connect the Lambda functions to your Redis database:
- REDIS_HOST: redis-18541.xxx.xxxx.xxx.cloud.redis.com
- REDIS_PORT: 18541
- REDIS_PASSWORD : <the password showed on the screen>
Step 2: Get the project from GitHub
Clone the repository to your local environment, and move it to the project directory
The project directory structure is shown here:
Step 3: Import the movie-database dataset into your application
The file aws-redis-cloud-demo/movies-list-microservice/import_movies.redis contains all the Redis commands to insert movies into the database. The commands used are:
To import the dataset, open a terminal and run the following command:
Step 4: Configure the application to use your Redis Enterprise Cloud instance
Before testing the application, you must configure the Node.js and Python services with your Redis Enterprise Cloud database instance. Open these files:
- ./movies-list-microservice/serverless.yml
- ./movie-comments-microservice/.chalice/config.json
Then set the Redis host, port, and password: (REDIS_HOST, REDIS_PORT, REDIS_PASSWORD)
Step 5: Build and run the movie microservice (Node.js)
Follow the steps listed here to build and run the project. (You can also find all the information in the project’s Readme file.)
- Install the serverless framework
2. Go to the movies-list-microservice directory
3. Install dependencies
4. Run the Lambda function locally
5. Test the service by opening a browser call to the REST service: http://localhost:3000/api/movies/1
6. Deploy the service to AWS, by running the following command to deploy the function to your AWS environment:
7. Test the API by pointing your browser to https://<xxx>.execute-api.<reg>.amazonaws.com/api/movies/1
Note: if you receive an error, check the functions log in AWS CloudWatch to see what happened.
A deeper look at the code:
- The package.json file contains the dependencies used by this Node.js project. This project is quite simple, and uses the following dependencies:
- The redis and redis-redisearch libraries are used to connect to Redis and exposed RediSearch commands.
- The aws-lambda library is used to call all the AWS Lambda functions to deploy a node application to your AWS environment.
- The serverless.yml file defines the serverless functions mapping HTTP actions to the JavaScript function that will be called (defined in handler.ts), and contains the environment variables (mostly a Redis connection string in this demonstration).
- The handler.ts file is the class that captures the event coming from the AWS Gateway and calls the application library SearchService, which is doing all the calls to the Redis database.
- The SearchService.ts file contains all the methods to interact with the Redis database and use the Redis and RediSearch API: client.ft_search(), client.aggregate(), client.hmset(), and more. (You can learn more about the Redis and RediSearch commands at Redis University and the Getting Started with RediSearch 2.0 tutorial on GitHub.
Step 6: Build and run the comments microservice (Python)
Here are the steps to build and run the project. (You can also find all the information in the project’s Readme file.)
- Move to the Python project and create a virtual environment:
2. Install the dependencies:
3. Set up the AWS environment, run the following command, and configure your ID and Secret:
4. Deploy the service to AWS, by running the following command to deploy the function to your AWS environment:
A deeper look at the code:
- The requirements.txt file contains the dependencies used by this Python project. This project is quite simple, and uses the following dependencies:
- Chalice is the AWS framework used to create serverless applications in Python
- redis and redisearch access Redis and use the RediSearch API
- The config.json file defines the serverless application and is used to define the environment variables—in this application, the Redis database connection information.
- The app.py file is the application entry point that defines all the REST endpoints using various routes. The application imports various dependencies, especially the CommentService that is used to interact with Redis. When you want to use multiple files you must put the files in the chalicelib folder.
- The comment_service.py file contains all the interactions with Redis to create, query and delete comments. An interesting point for the comment feature is the search() method. This method is used to retrieve the comments for a movie sorted by the date of creation using a search_client.search() call.
Optionally, you can store the Redis database password in AWS Key Management Service. You can find the configuration steps in the project documentation.
Step 7: Run the frontend application
- Go to the frontend directory and install the dependencies:
2. Edit the .env.development file to set the URL of the movie and comment services:
3. Run the application:
4. Open your browser, and go to http://localhost:8084
You can now navigate in the application, update and search movies, and add/delete comments.
Optionally, you can use S3 and CloudFront to deploy the Vue application in your AWS environment and serve it publicly to your users. This is explained in the project documentation.
Conclusion
Working with AWS Lambda and Redis Enterprise Cloud simplifies the deployment of your services. Using Redis Enterprise Cloud with RediSearch, you can easily query Redis data using values, allowing you to use Redis as the main database of your services.
Redis Enterprise Cloud is compatible with Redis, allowing you to easily migrate your existing Redis deployments, both OSS and managed services. You just need to change the connection parameters (such as database endpoints). There are multiple ways to perform a live migration, including:
- Blue-green deployments
- Synchronizing Amazon ElastiCache and Redis Enterprise Cloud using Active Passive Geo-Distribution
- Using our open source RIOT tool to migrate your data
In addition to RediSearch, Redis Enterprise Cloud lets you use other promising data models such as graph, JSON, time series, and Bloom filters, and offers a wide variety of other database features critical in production environments, including high availability, scalability, persistence, security, and Active-Active geo-distribution.
Want to learn more? Check out our AWS re:Invent home page and read these tutorials and blog posts:
Get started with Redis today
Speak to a Redis expert and learn more about enterprise-grade Redis today.
