Blog
Building a Context-Enabled Semantic Cache with Redis
Generative AI has rapidly evolved into the spotlight of enterprise innovation, transforming everything from customer service to internal knowledge management. Yet, enterprises face emerging issues with large language models in production: high operational costs, slow response times, and generic, impersonal outputs. Previously, most solutions could solve for only a subset of these, usually at the behest of the others. For example, premium model calls are used with complex prompting to solve generic outputs. Solving operational costs meant using fewer premium model calls, increasing latency, and lowering quality outputs. To overcome these challenges, we’ve introduced an innovative architecture called Context-Enabled Semantic Caching (CESC), leveraging the powerful combination of OpenAI models and Redis.
The Evolution of Caching: From rigid key-value pairs to flexible meaning-based retrieval
To understand the power of CESC, it helps to see the evolution of caching.
First, there's traditional data caching, which we've used for decades. It works on exact matches. The system stores the result if you request data with the key user:123. The next time the exact same key user:123 is requested, you get a near-instant response from the cache. It's incredibly fast but completely rigid; a query for user:124 is a total cache miss and a new call to the database.
Next came traditional semantic caching, a massive leap forward for AI applications. It works on semantic meaning using vector embeddings of responses, not exact matches. For example:
- Query 1: An employee asks an HR bot for the first time, "What is the company policy on parental leave?"
- The application checks Redis and is empty. This is a cache miss. The query goes to the LLM model (i.e., GPT-4o), which generates an answer, and the result is cached.
- Query 2: A different employee asks the chatbot, "Tell me about our rules for taking time off after having a baby."
- The application checks Redis and finds the vector embeddings of Query 1's request and response (“What is the company policy on parental leave?”). Even though the words are different, the intent is the same. This is a semantic cache hit. The cached answer from Query 1's response is served in milliseconds, the LLM is never called for this query, and zero tokens are consumed, saving significant time and cost.
This is a huge improvement, but it still has a critical limitation: the cached response is generic. What if the employees asking are in different states with different laws? Traditional semantic caching can't bridge this personalization gap on its own, and this is where Context-Enabled Semantic Caching comes in.
Introducing Context-Enabled Semantic Caching (CESC)
While traditional semantic caching offers substantial efficiency and cost benefits, Context-Enabled Semantic Caching (CESC) takes this further by embedding personalized user context and relevant information directly into cached responses. This significantly boosts accuracy, reduces latency even more, and cuts operational expenses further by optimizing model usage.
- Traditional Cache → Exact Match → Fast but brittle
- Semantic Cache → Meaning Match → Fast and flexible
- Context-Enabled Cache → Meaning + Context → Fast, personalized, efficient
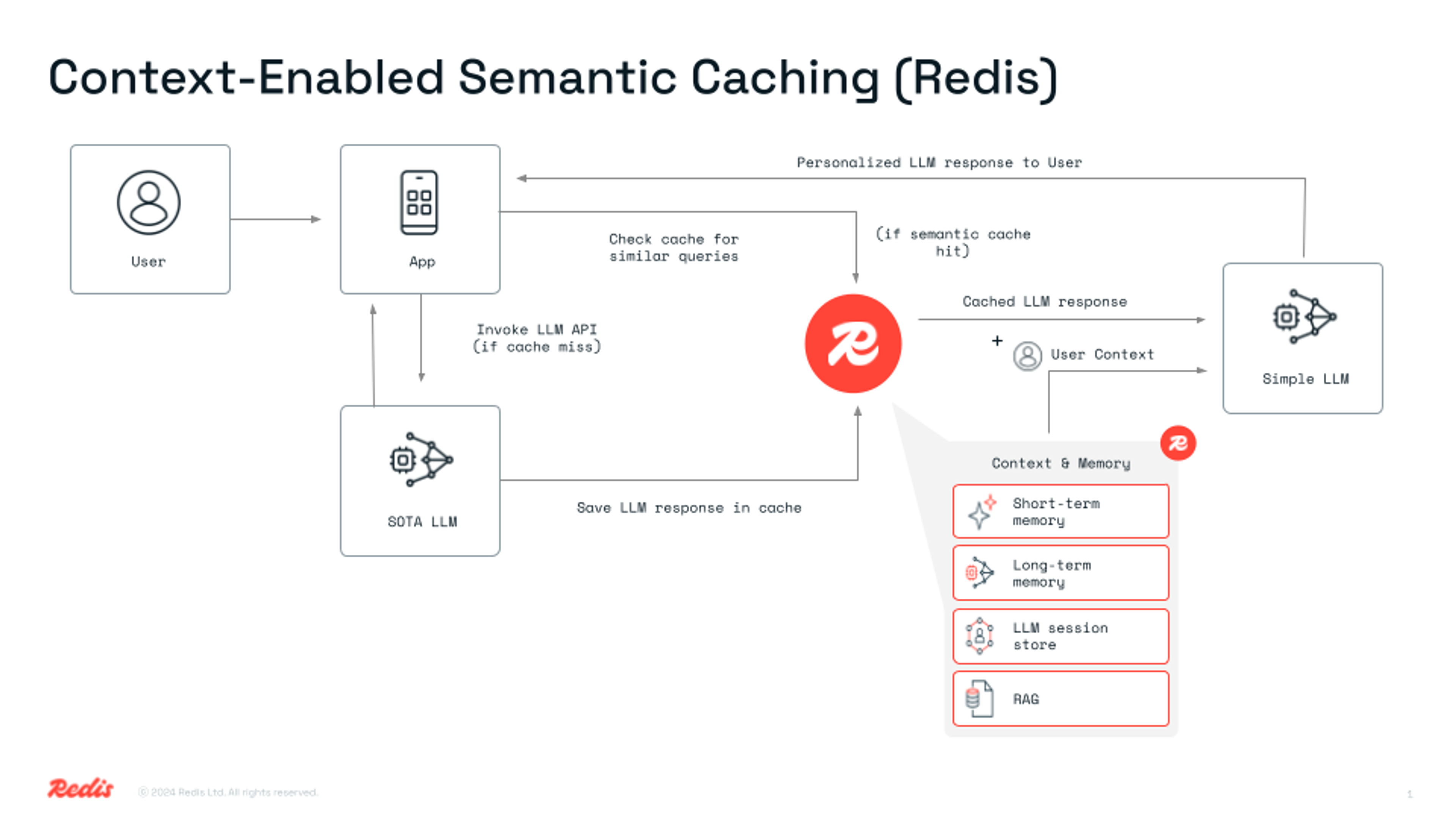
How does this work? Picking up from our previous examples, when a query had a semantic cache hit, the process would previously have ended there. Instead, in CESC, we take that semantic cache hit response, plus any context stored (user profile, chat history, user preferences, RAG data on enterprise knowledge, etc.), and send those as inputs to a simpler, cheaper LLM model, for real-time personalization and augmentation.
This is achieved through a multi-layer architecture:
- Semantic Similarity Cache: The foundation, using RedisVL on Redis to find a conceptually similar answer that has been previously generated.
- User Context Memory: A high-speed Redis data structure that stores key-value information about the user, their role, location, department, etc.
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Context: In parallel, this layer can retrieve relevant, real-time information from a separate enterprise knowledge base (e.g., product docs, company policies, support articles), also indexed in Redis.
- Real-Time Personalization & Augmentation Layer: A lightweight OpenAI model (gpt-4o-mini) that takes the generic cached response, the user context, and the RAG context, then instantly synthesizes them into a hyper-personalized and factually augmented response.
Technical Deep Dive: How CESC Works
Redis seamlessly integrates RedisVL for vector search and semantic lookups. Embeddings from OpenAI’s text-embedding-small model enable fast similarity searches, drastically improving cache hit rates.
Here’s a simplified view of the architecture:
Why This Architecture Matters to Enterprises
Modern enterprises operate at scale, requiring consistent and efficient access to information across roles, departments, and geographies. Context-Enabled Semantic Caching solves a spectrum of enterprise challenges by:
- Scaling AI Cost-Effectively: CESC enables large-scale deployment of generative AI without linearly increasing costs, thanks to the efficient use of cached knowledge and lightweight personalization models.
- Enhancing Workforce Productivity: Employees spend less time waiting for generic responses and more time acting on precise, role-relevant information. This compounding time savings leads to significant productivity gains.
- Improving Governance and Consistency: Cached and personalized outputs can be audited, versioned, and aligned with company policy—something difficult to enforce in stateless, one-off LLM calls.
- Creating Differentiated Experiences: Whether powering an employee chatbot, customer self-service, or developer tooling, CESC allows organizations to offer AI responses that feel custom-built for every user.
This architecture enables enterprises to move beyond basic AI integration into operationalized, high-performance AI applications that are cost-aware, secure, and hyper-personalized.
Real-World Example: Enterprise IT Support Chatbot
Imagine Maria, an IT support specialist at a large company, querying her internal chatbot: “A user in the finance department can't access the dashboard — what should I check?” What do we know about Maria? Stored in our Redis memory, we know her users are on Chrome on macOS, she resolves access issues efficiently for finance team users, and she frequently solves issues with the ‘finance_dashboard_viewer’role misconfigurations. Here is what a hypothetical scenario would look like:
(*Pre-condition: The previous response needs to have already been asked and stored in Redis)
- Plain LLM, Without CESC: Maria or any user in the company waits 2-3 seconds for a generic, detailed GPT-4o-generated guide.
- “First, verify the user's permissions and access rights to the dashboard in the system settings. Ensure they are assigned the correct role or group. Next, check for any connectivity issues, browser compatibility, or recent changes to the dashboard configuration that might affect access.”
- Latency: ~2s | Cost: ~100 tokens
- With Traditional Semantic Caching*: If Maria or another user asks the same type of question, they quickly get the generic cached response, which is slightly faster but still generic.
- Same output as plain LLM, semantic cache hit
- Latency: <1ms | Cost: 0 tokens
- With CESC*: Maria receives a personalized response tailored to her role, her department’s specific procedures, and previous interactions.
- “First, check the user's permissions to ensure they have the 'finance_dashboard_viewer' role correctly assigned in the system settings. Since they’re using Chrome on macOS, confirm there are no browser compatibility issues and that your SSO is functioning properly. Lastly, review any recent configuration changes that might impact access to the dashboard.”
- Latency: ~90ms | Cost: ~300 tokens, but for a model that costs ~10% the price per token
This improvement isn’t just convenient; it significantly boosts productivity and reduces operational expenses.
Quantifiable Benefits for Enterprises
CESC directly addresses key enterprise concerns:
- User Personalization: Providing a customized and personalized response at 70-90% cheaper costs unlocks numerous enterprise use cases.
- Reduced Latency: Even with an additional LLM call, the personalized response can be up to 40% faster than a fresh premium LLM call, due to the prompt already having all inputs required, and the lightweight model refinement.
- Enhanced Productivity: Employees gain immediate, relevant information, minimizing downtime and boosting operational efficiency.
Getting Started with CESC
Follow these steps to prototype CESC in your environment quickly:
- Deploy Redis Cloud.
- Set up RedisVL 0.8 via pip and initialize vector indexes.
- Configure OpenAI endpoints (GPT-4o, GPT-4o-mini, text-embedding-small) or similar LLMs.
- Explore our upcoming public demo notebooks (links coming soon).
Stay tuned as we continue enhancing this innovative architecture.
Resources
Questions or ready to dive deeper? Reach out directly, and let’s redefine how your enterprise leverages AI.
Get started with Redis today
Speak to a Redis expert and learn more about enterprise-grade Redis today.
