Connect to your Active-Active databases
How to connect to an Active-Active database using redis-cli or a sample Python application.
| Redis Software |
|---|
With the Redis database created, you are ready to connect to your database to store data. You can use one of the following ways to test connectivity to your database:
- Connect with redis-cli, the built-in command-line tool
- Connect with a Hello World application written in Python
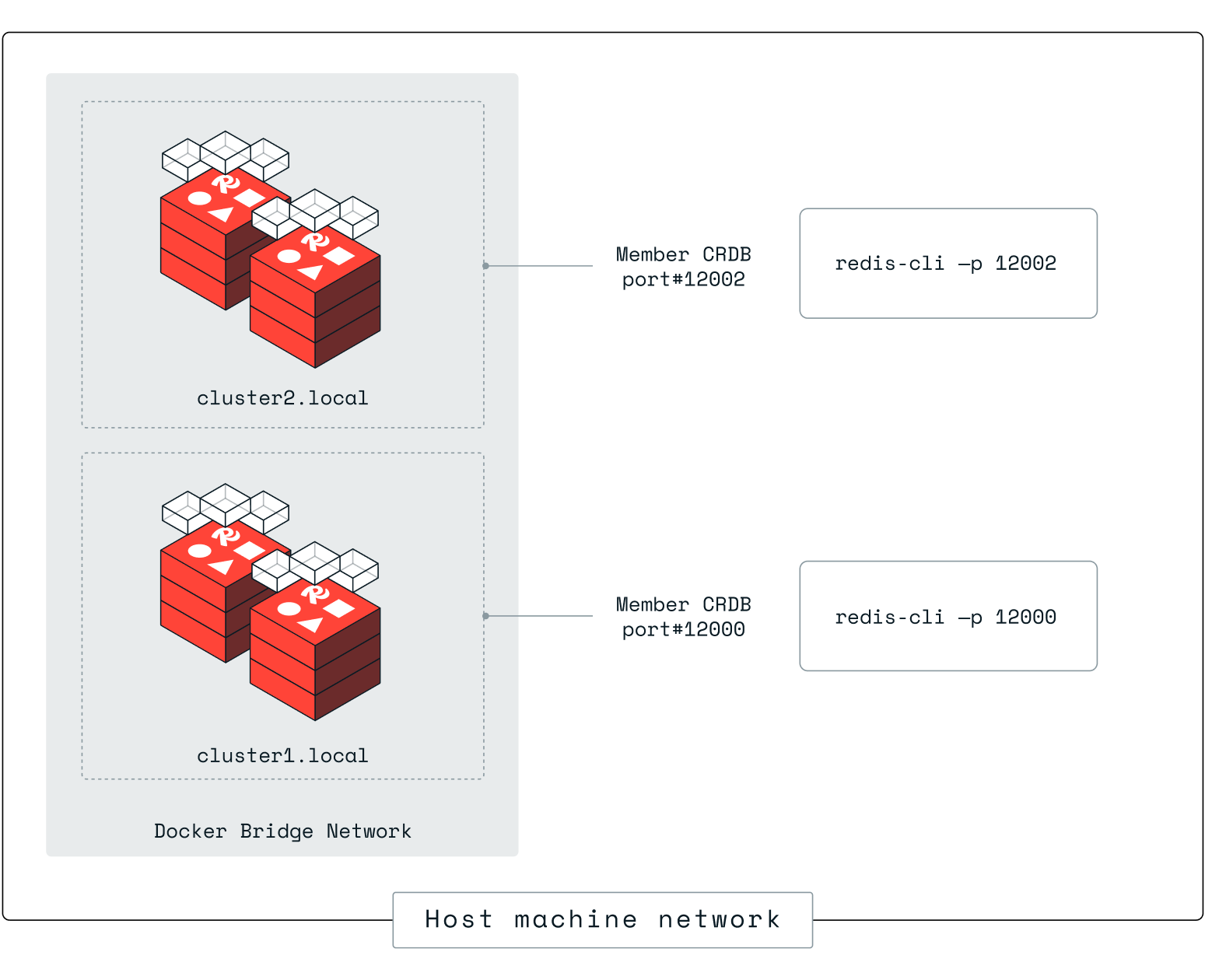
Remember we have two member Active-Active databases that are available for connections and concurrent reads and writes. The member Active-Active databases are using bi-directional replication to for the global Active-Active database.
Connecting using redis-cli
redis-cli is a simple command-line tool to interact with redis database.
-
To use redis-cli on port 12000 from the node 1 terminal, run:
redis-cli -p 12000 -
Store and retrieve a key in the database to test the connection with these commands:
set key1 123get key1
The output of the command looks like this:
127.0.0.1:12000> set key1 123 OK 127.0.0.1:12000> get key1 "123" -
Enter the terminal of node 1 in cluster 2, run the redis-cli, and retrieve key1.
The output of the commands looks like this:
$ redis-cli -p 12000 127.0.0.1:12000> get key1 "123"
Connecting using Hello World application in Python
A simple python application running on the host machine can also connect to the database.
-
In the command-line terminal, create a new file called "redis_test.py"
vi redis_test.py -
Paste this code into the "redis_test.py" file.
This application stores a value in key1 in cluster 1, gets that value from key1 in cluster 1, and gets the value from key1 in cluster 2.
import redis rp1 = redis.StrictRedis(host='localhost', port=12000, db=0) rp2 = redis.StrictRedis(host='localhost', port=12002, db=0) print ("set key1 123 in cluster 1") print (rp1.set('key1', '123')) print ("get key1 cluster 1") print (rp1.get('key1')) print ("get key1 from cluster 2") print (rp2.get('key1')) -
To run the "redis_test.py" application, run:
python redis_test.pyIf the connection is successful, the output of the application looks like:
set key1 123 in cluster 1 True get key1 cluster 1 "123" get key1 from cluster 2 "123"