Tutorial
Redis Time Series
February 26, 20265 minute read
TL;DR:Redis Time Series is a Redis module purpose-built for ingesting, querying, and aggregating time-series data such as IoT sensor readings, stock prices, and application telemetry. It supports built-in downsampling, aggregation, and labeling so you can store millions of data points with a small memory footprint and query them at Redis speed.
NOTERedis now supports time series data structures natively without the need for a module
#What you'll learn
- What Redis Time Series is and when to use it
- How to create time series keys with
TS.CREATE - How to add data points with
TS.ADD - How to query ranges and get the latest value with
TS.RANGEandTS.GET - How to filter time series using labels with
TS.MGET - How to apply aggregation and downsampling to time-series queries
#What is Redis Time Series?
Redis Time Series is a Redis module that enhances your experience managing time-series data with Redis. It simplifies the use of Redis for time-series use cases such as internet of things (IoT) data, stock prices, and telemetry. With Redis Time Series, you can ingest and query millions of samples and events at the speed of Redis. Advanced tooling such as downsampling and aggregation ensure a small memory footprint without impacting performance. Use a variety of queries for visualization and monitoring with built-in connectors to popular monitoring tools like Grafana, Prometheus, and Telegraf.
Compared to general-purpose time-series databases, Redis Time Series offers sub-millisecond reads and writes, built-in downsampling rules that reduce storage without a separate ETL pipeline, and a label-based filtering system that makes it easy to query across thousands of keys at once.
#Step 1. Register and subscribe
Follow this link to register and subscribe to Redis Cloud
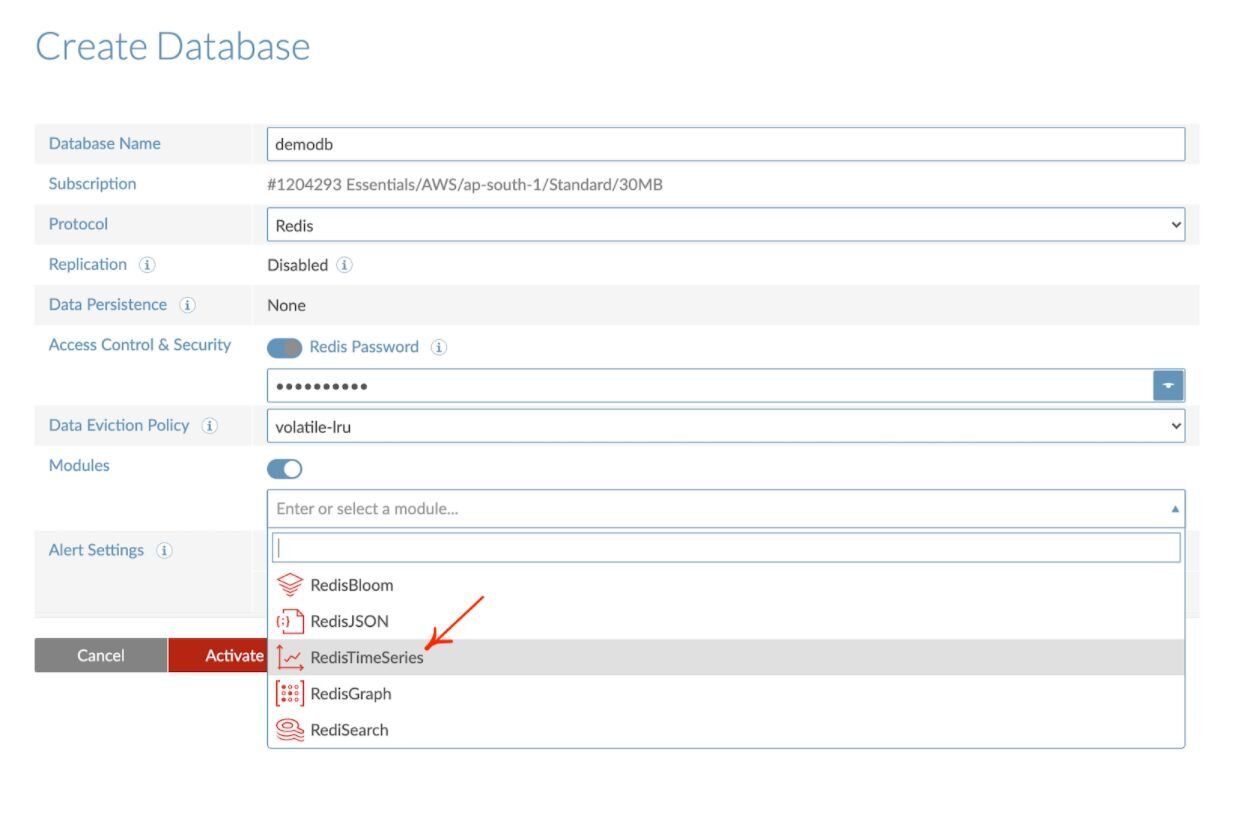
#Step 2. Create a database with Redis time series
#Step 3. Connect to a database
Follow this link to learn how to connect to a database
#Step 4. Getting Started with Redis time series
This section will walk you through using some basic Redis time series commands. You can run them from the Redis command-line interface (redis-cli) or use the CLI available in Redis Insight. (See part 2 of this tutorial to learn more about using the Redis Insight CLI.) Using a basic air-quality dataset, we will show you how to:
- Create a new time series
- Add a new sample to the list of series
- Query a range across one or multiple time series

#Create a new time series
Let's create a time series representing air quality dataset measurements. To interact with Redis time series you will most often use the TS.RANGE command, but here you will create a time series per measurement using the TS.CREATE command. Once created, all the measurements will be sent using TS.ADD.
The sample command below creates a time series and populates it with three entries:
In the above example, ts:carbon_monoxide, ts:relative_humidity and ts:temperature are key names. We are creating a time series with two labels (sensor_id and area_id are the fields with values 2 and 32 respectively) and a retention window of 60 milliseconds:
#Add a new sample data to the time series
Let's start to add samples into the keys that will be automatically created using this command:
#Querying the sample
Now that you have sample data in your time series, you're ready to ask questions such as:
#How do you get the last sample from a Redis time series?
TS.GET is used to get the last sample. The returned array will contain the last sample timestamp followed by the last sample value, when the time series contains data:#How do you get the last sample matching a specific filter?
TS.MGET is used to get the last samples matching the specific filter:#How do you get samples with labels matching a specific filter?
#How do you query a range across one or more time series?
TS.RANGE is used to query a range in forward directions while TS.REVRANGE is used to query a range in reverse directions. They let you answer such questions as:#How do you get samples for a time range?
#How do you use aggregation with Redis time series?
You can use various aggregation types such as avg, sum, min, max, range, count, first, last etc. The example below shows how to use the
avg aggregation type to downsample your data:#Next steps
- Learn more about Redis time series in the Redis quick start tutorial
- Build a real-time API with time-series data using FastAPI and Redis
- Explore the time series data type documentation for the full command reference
- Connect Redis Time Series to Grafana for real-time dashboards and monitoring