Graph quick start
Graph quick start
Prerequisites
For this quick start tutorial, you need:
-
A Redis database with the RedisGraph module enabled. You can use either:
-
A Redis Cloud database
-
A Redis Software database
-
-
redis-clicommand-line tool -
redis-pyclient library v4.1.0 or later
Graph with redis-cli
To begin, connect to your database with redis-cli.
Create a graph
When you create a graph, you can define nodes and the relationships between them with this format:
(:<node 1>)-[:<relationship>]->(:<node 2>)
To define multiple nodes and relationships in a single creation query, separate the entries with commas.
For example, use the CREATE query to create a new graph of motorcycle riders and teams participating in the MotoGP league:
127.0.0.1:12543> GRAPH.QUERY MotoGP "CREATE (:Rider {name:'Valentino Rossi'})-[:rides]->(:Team {name:'Yamaha'}), (:Rider {name:'Dani Pedrosa'})-[:rides]->(:Team {name:'Honda'}), (:Rider {name:'Andrea Dovizioso'})-[:rides]->(:Team {name:'Ducati'})"
1) 1) "Labels added: 2"
2) "Nodes created: 6"
3) "Properties set: 6"
4) "Relationships created: 3"
5) "Cached execution: 0"
6) "Query internal execution time: 0.385472 milliseconds"
Add nodes
You can add new nodes to a previously created graph:
127.0.0.1:12543> GRAPH.QUERY MotoGP "CREATE (:Rider {name:'Jorge Lorenzo'})"
1) 1) "Nodes created: 1"
2) "Properties set: 1"
3) "Cached execution: 0"
4) "Query internal execution time: 0.185841 milliseconds"
Add relationships
To create new relationships between nodes of a graph:
127.0.0.1:12543> GRAPH.QUERY MotoGP "MATCH (r:Rider), (t:Team) WHERE r.name = 'Jorge Lorenzo' and t.name = 'Honda' CREATE (r)-[:rides]->(t)"
1) 1) "Relationships created: 1"
2) "Cached execution: 0"
3) "Query internal execution time: 0.356578 milliseconds"
Query the graph
After you create a graph, you can use the GRAPH.QUERY command to query the graph's data.
The following example returns which motorcycle riders compete for team Yamaha:
127.0.0.1:12543> GRAPH.QUERY MotoGP "MATCH (r:Rider)-[:rides]->(t:Team) WHERE t.name = 'Yamaha' RETURN r,t"
1) 1) "r"
2) "t"
2) 1) 1) 1) 1) "id"
2) "0"
2) 1) "labels"
2) 1) "Rider"
3) 1) "properties"
2) 1) 1) "name"
2) "Valentino Rossi"
2) 1) 1) "id"
2) "1"
2) 1) "labels"
2) 1) "Team"
3) 1) "properties"
2) 1) 1) "name"
2) "Yamaha"
3) 1) "Cached execution: 0"
2) "Query internal execution time: 0.500535 milliseconds"
You can also use functions to create more complex queries.
For example, you can use the count function to check how many riders represent team Honda:
127.0.0.1:12543> GRAPH.QUERY MotoGP "MATCH (r:Rider)-[:rides]->(t:Team {name:'Honda'}) RETURN count(r)"
1) 1) "count(r)"
2) 1) 1) "2"
3) 1) "Cached execution: 0"
2) "Query internal execution time: 0.445760 milliseconds"
Delete nodes
You can use the DELETE query to remove a specific node and its relationships from the graph:
127.0.0.1:12543> GRAPH.QUERY MotoGP "MATCH (r:Rider {name: 'Dani Pedrosa'}) DELETE r"
1) 1) "Nodes deleted: 1"
2) "Relationships deleted: 1"
3) "Cached execution: 0"
4) "Query internal execution time: 0.276815 milliseconds"
Delete relationships
You can also use the DELETE query to delete a node's relationships without removing any nodes:
127.0.0.1:12543> GRAPH.QUERY MotoGP "MATCH (:Rider {name: 'Valentino Rossi'})-[r:rides]->() DELETE r"
1) 1) "Relationships deleted: 1"
2) "Cached execution: 0"
3) "Query internal execution time: 0.348346 milliseconds"
Delete a graph
To delete an entire graph, including all nodes and relationships, run the GRAPH.DELETE command:
127.0.0.1:12543> GRAPH.DELETE MotoGP
"Graph removed, internal execution time: 0.013138 milliseconds"
Graph with Python
If you want to use graphs within an application, you can use one of these client libraries.
The following example uses the Redis Python client library redis-py, which supports graph commands as of v4.1.0.
This Python code creates a graph that represents friendships between users on a social media website. It also shows how to run queries and change relationships between users.
import redis
from redis.commands.graph.edge import Edge
from redis.commands.graph.node import Node
# Connect to a database
r = redis.Redis(host="<endpoint>", port="<port>",
password="<password>")
# Create nodes that represent users
users = { "Alex": Node(label="Person", properties={"name": "Alex", "age": 35}),
"Jun": Node(label="Person", properties={"name": "Jun", "age": 33}),
"Taylor": Node(label="Person", properties={"name": "Taylor", "age": 28}),
"Noor": Node(label="Person", properties={"name": "Noor", "age": 41}) }
# Define a graph called SocialMedia
social_graph = r.graph("SocialMedia")
# Add users to the graph as nodes
for key in users.keys():
social_graph.add_node(users[key])
# Add relationships between user nodes
social_graph.add_edge( Edge(users["Alex"], "friends", users["Jun"]) )
# Make the relationship bidirectional
social_graph.add_edge( Edge(users["Jun"], "friends", users["Alex"]) )
social_graph.add_edge( Edge(users["Jun"], "friends", users["Taylor"]) )
social_graph.add_edge( Edge(users["Taylor"], "friends", users["Jun"]) )
social_graph.add_edge( Edge(users["Jun"], "friends", users["Noor"]) )
social_graph.add_edge( Edge(users["Noor"], "friends", users["Jun"]) )
social_graph.add_edge( Edge(users["Alex"], "friends", users["Noor"]) )
social_graph.add_edge( Edge(users["Noor"], "friends", users["Alex"]) )
# Create the graph in the database
social_graph.commit()
# Query the graph to find out how many friends Alex has
result1 = social_graph.query("MATCH (p1:Person {name: 'Alex'})-[:friends]->(p2:Person) RETURN count(p2)")
print("Alex's original friend count:", result1.result_set)
# Delete a relationship without deleting any user nodes
social_graph.query("MATCH (:Person {name: 'Alex'})<-[f:friends]->(:Person {name: 'Jun'}) DELETE f")
# Query the graph again to see Alex's updated friend count
result2 = social_graph.query("MATCH (p1:Person {name: 'Alex'})-[:friends]->(p2:Person) RETURN count(p2)")
print("Alex's updated friend count:", result2.result_set)
# Delete the entire graph
social_graph.delete()
Example output:
$ ./quick_start.py
Alex's original friend count: [[2]]
Alex's updated friend count: [[1]]
Visualize graphs with Redis Insight
You can use the Redis Insight workbench to visualize the relationships between the nodes of your graph.
-
Connect to your database with Redis Insight. You can connect manually or use the auto-discovery feature.
-
Select the Workbench button.
-
Enter a graph query in the text editor.
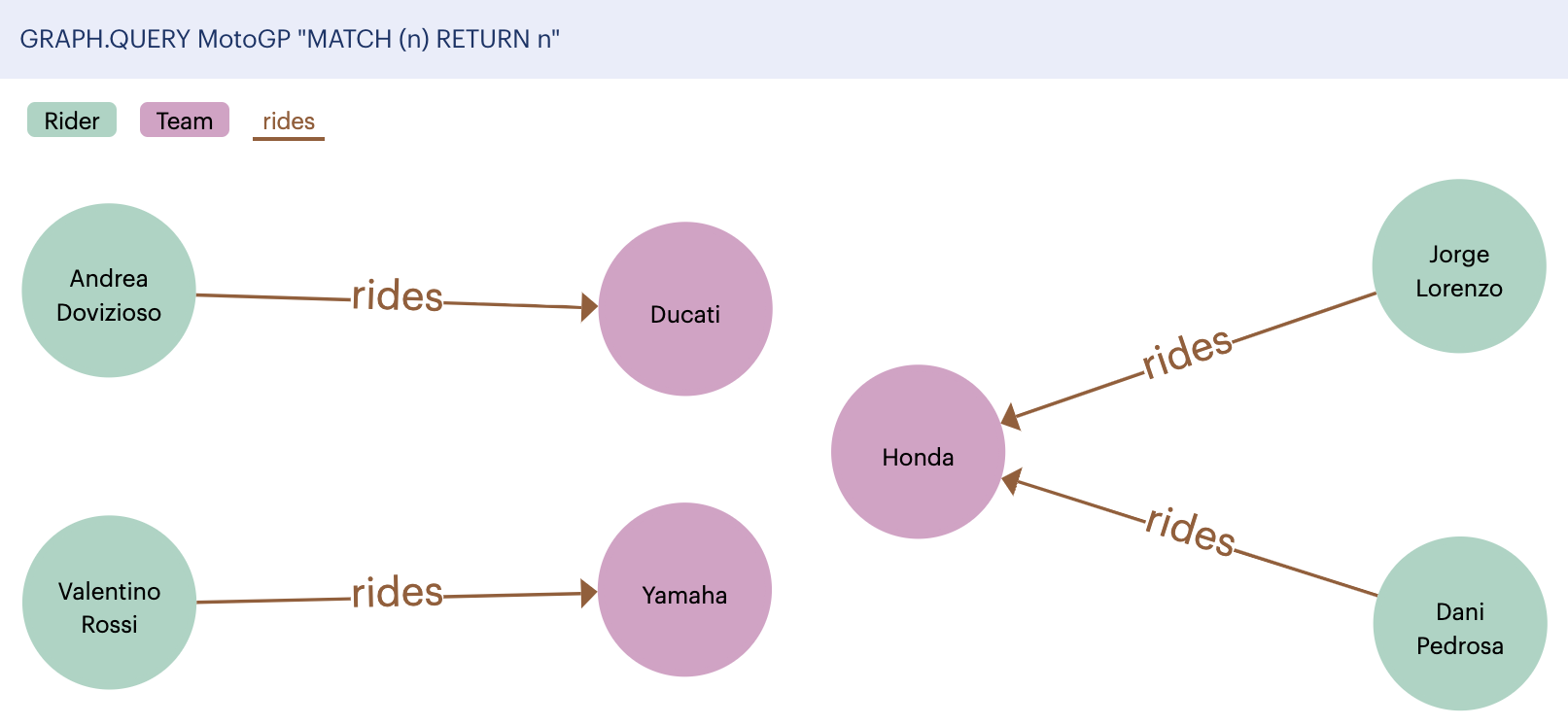
For example, this query returns all nodes and relationships in the graph:
GRAPH.QUERY MotoGP "MATCH (n) RETURN n" -
Select Run to run the query.
After you run a query, the output log displays a visual representation of your graph's nodes and relationships: