Set up a Redis Software cluster behind a load balancer
Set up a Redis Software cluster using a load balancer instead of DNS to direct traffic to cluster nodes.
| Redis Software |
|---|
To set up a Redis Software cluster in an environment that doesn't allow DNS, you can use a load balancer (LB) to direct traffic to the cluster nodes.
DNS role for databases
Normally, Redis Software uses DNS to provide dynamic database endpoints.
A DNS name such as redis-12345.clustername.domain gives clients access to the database resource:
- If multiple proxies are in use, the DNS name resolves to multiple IP addresses so clients can load balance.
- On failover or topology changes, the DNS name is automatically updated to reflect the live IP addresses.
When DNS cannot be used, clients can still connect to the endpoints with the IP addresses, but the benefits of load balancing and automatic updates to IP addresses won't be available.
Network architecture with load balancer
You can compensate for the lack of DNS resolution with load balancers that can expose services and provide service discovery. A load balancer is configured in front of the Redis Software cluster, exposing several logical services:
- Control plane services, such as the Cluster Manager UI
- Data plane services, such as database endpoints for client application connections
Depending on which Redis Software services you want to access outside the cluster, you may need to configure the load balancers separately. One or more virtual IPs (VIPs) are defined on the load balancer to expose Redis Software services. The architecture is shown in the following diagram with a 3-node Redis Software cluster with one database (DB1) configured on port 12000:
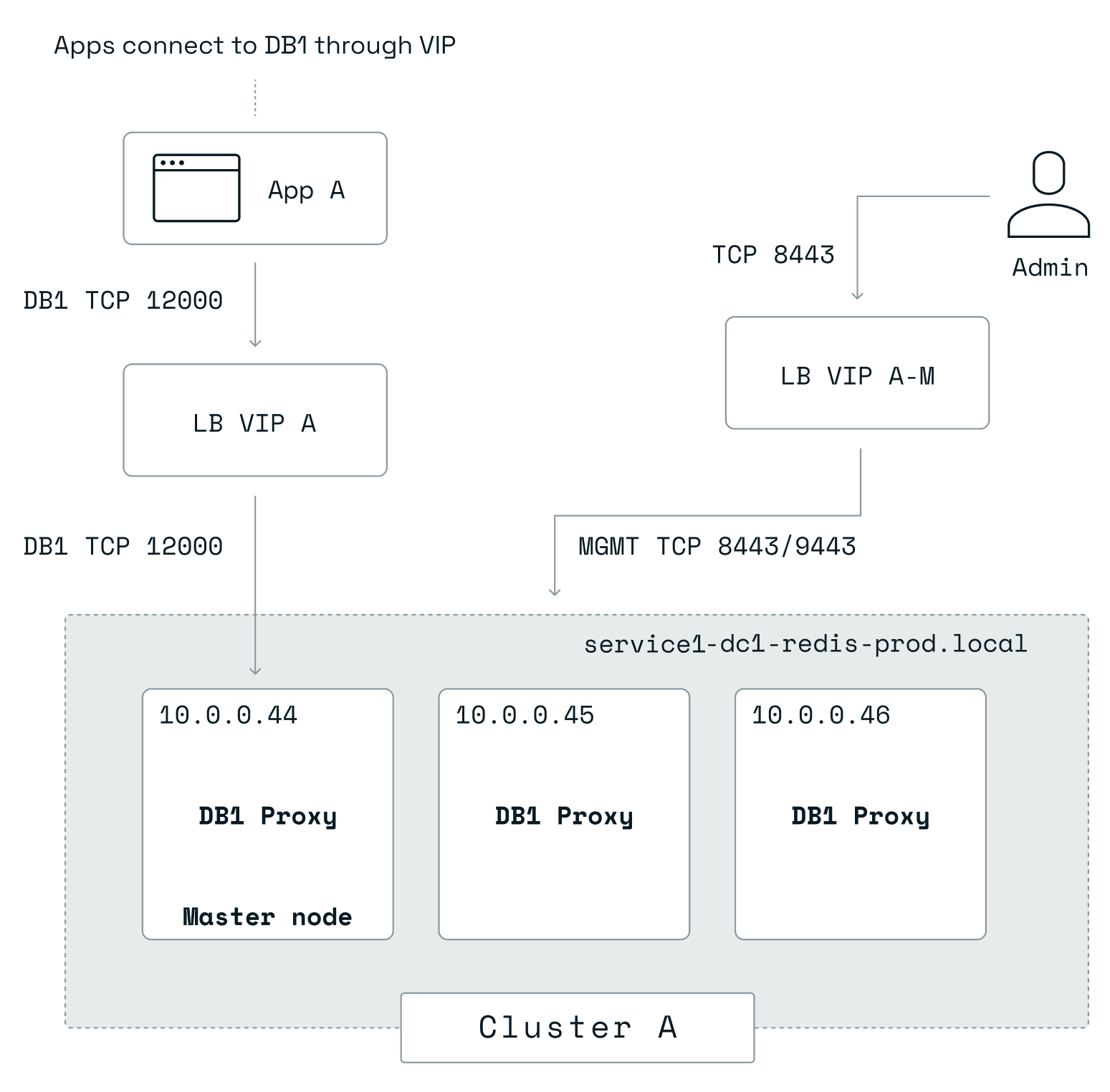
Set up a cluster with load balancers
Prerequisites
- Install the latest version of Redis Software on your clusters
- Configure the cluster with the cluster name (FQDN) even though DNS is not in use. Remember that the same cluster name is used to issue the license keys. We recommend that you use a ".local" suffix in the FQDN.
Configure load balancers
- Make sure that the load balancer is performing TCP health checks on the cluster nodes.
- Expose the services that you require through a virtual IP, for example:
- Cluster Manager UI on port 8443
- Rest API on port 9443 for secure HTTPS connections and port 8080 for HTTP
- Database ports 10000-19999
Other ports are shown in the list of Redis Software network ports.
Sticky, secured connections are needed only for the Redis Software Cluster Manager UI on port 8443.
- Certain load balancers provide specific logic to close idle connections. Either turn off this feature or make sure the applications connecting to Redis use reconnection logic.
- Make sure the load balancer is fast enough to resolve connections between two clusters or applications that are connected to Redis databases through a load balancer.
- Choose the standard load balancer that is commonly used in your environment so that you have easy access to in-house expertise for troubleshooting issues.
Configure cluster
For clusters behind load balancers, we recommend using the all-nodes proxy policy and enabling handle_redirects.
To allow inbound connections to be terminated on the relevant node inside the cluster, run the following rladmin commands on the cluster:
# Enable all-nodes proxy policy by default
rladmin tune cluster default_sharded_proxy_policy all-nodes default_non_sharded_proxy_policy all-nodes
# Redirect where necessary when behind a load balancer
rladmin cluster config handle_redirects enabled
Optionally configure sparse shard placement to allow closer termination of client connections to where the Redis shard is located:
# Enable sparse placement by default
rladmin tune cluster default_shards_placement sparse
Configure database
After you update the cluster settings and configure the load balancers, you can go to the Redis Software Cluster Manager UI at https://load-balancer-virtual-ip:8443/ and create a new database.
To create an Active-Active database, use the crdb-cli utility. See the crdb-cli reference for more information about creating Active-Active databases from the command line.
Update load balancer configuration when cluster configuration changes
When your Redis Software cluster is behind a load balancer, you must update the load balancer when the cluster topology and IP addresses change. Some common cases that require you to update the load balancer are:
- Adding new nodes to the Redis Software cluster
- Removing nodes from the Redis Software cluster
- Maintenance for Redis Software cluster nodes
- IP address changes for Redis Software cluster nodes
After these changes, make sure that the Redis connections in your applications can connect to the Redis database, especially if they are directly connected on IP addresses that have changed.
Intercluster communication considerations
Redis Software supports several topologies that allow intercluster replication, such as Replica Of and Active-Active deployment options. When your Redis Software clusters are behind load balancers, you must allow some network services to be open and defined in the load balancers to allow the replication to work.
Replica Of
For Replica Of communication to work, you must expose database ports locally in each cluster and allow these ports through any firewalls between the clusters.
Active-Active
For Active-Active communication to work, you must expose several ports, including every database port and several control plane ports as defined in Network port configurations. Pay attention to services that include "Active-Active" in the connection source column, and allow these ports through any firewalls between the clusters.