Access control
An overview of access control in Redis Software.
| Redis Software |
|---|
Redis Software lets you use role-based access control (RBAC) to manage users' access privileges. RBAC requires you to do the following:
-
Create roles and define each role's access privileges.
-
Create users and assign roles to them. The assigned role determines the user's access privileges.
Cluster access versus database access
Redis Software allows two separate paths of access:
-
Cluster access allows performing management-related actions, such as creating databases and viewing statistics.
-
Database access allows performing data-related actions, like reading and writing data in a database.
You can grant cluster access, database access, or both to each role. These roles let you differentiate between users who can access databases and users who can access cluster management, according to your organization's security needs.
The following diagram shows three different options for roles and users:
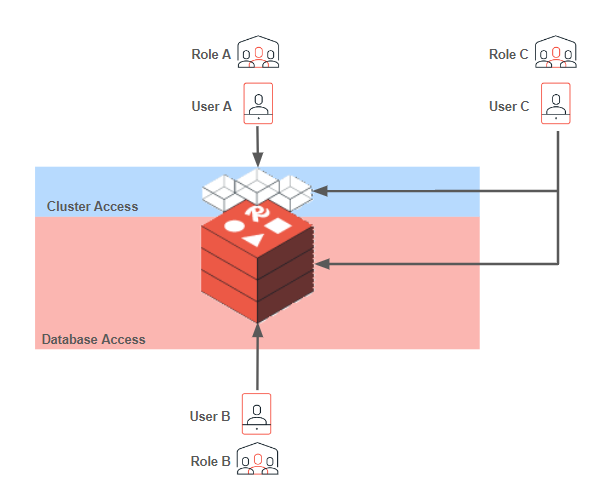
-
Role A was created with permission to access the cluster and perform management-related actions. Because user A was assigned role A, they can access the cluster but cannot access databases.
-
Role B was created with permission to access one or more databases and perform data-related actions. Because user B was assigned role B, they cannot access the cluster but can access databases.
-
Role C was created with cluster access and database access permissions. Because user C was assigned role C, they can access the cluster and databases.
Default database access
When you create a database, default user access is enabled automatically.
If you set up role-based access controls for your database and don't require compatibility with versions earlier than Redis 6, you can deactivate the default user.