For developersBuild 5 Rate Limiters with Redis: Fixed Window, Sliding Window, Token Bucket, and Leaky Bucket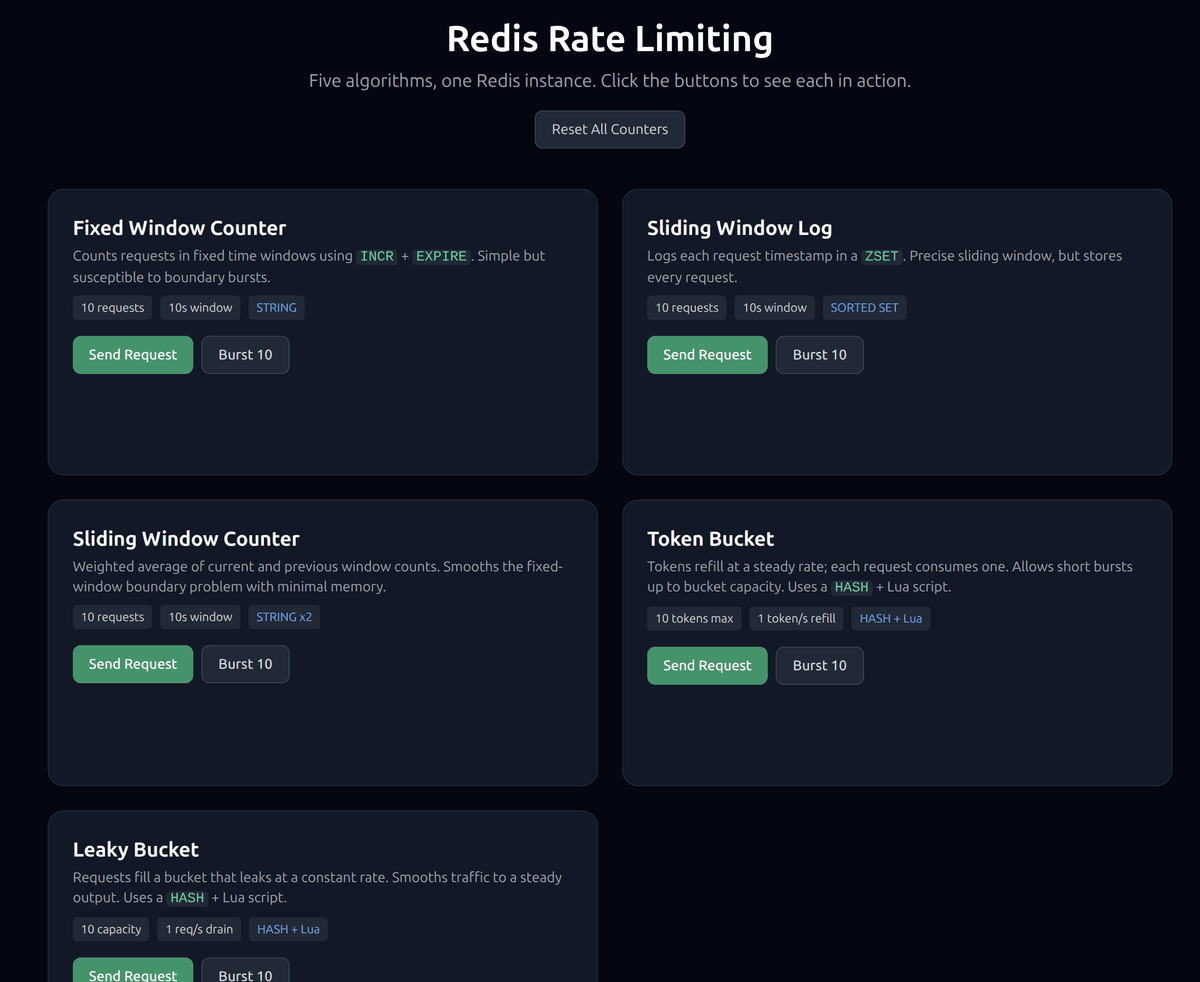

Note: This tutorial uses the code from the following git repository:https://github.com/redis-developer/redis-ratelimiting-js
Rate limiting controls how many requests a client can make in a given time period. It protects APIs from abuse, ensures fair usage across consumers, and prevents a single bad actor from overwhelming your infrastructure. Redis is a natural fit for this job — it's fast, supports atomic operations like
INCR, and has built-in key expiration via TTL.In this tutorial you'll build five different rate limiters, each using a different Redis data structure and algorithm. By the end you'll understand the trade-offs between them and know which one to reach for in your own apps.
#Prerequisites
- bun (v1.2+)
- Docker (optional, for running Redis locally)
- A Redis instance — either local via Docker or a free Redis Cloud database
- Basic familiarity with JavaScript/TypeScript and Lua
#Setup
Clone the repo and install dependencies:
Copy the example env file and set your Redis connection string:
Your
.env should contain:Note: If you use Redis Cloud, replace the URL in your .env and .env.docker with your Redis Cloud connection string. See the Connecting to a Redis Cloud database doc for details.
Start the app with Docker:
#How the demo works
Each rate limiter exposes an
attempt(key, config) function that returns a consistent result:The demo app serves a UI at
http://localhost:8080 where you can click Send Request or Burst 10 for each algorithm and see the results in real time.#1. Fixed window counter
#How it works
Divide time into fixed-length windows (e.g. 10-second blocks). Each window gets a counter. Every request increments the counter, and once it exceeds the limit the request is denied. The counter key includes the window number, so a new window automatically starts a fresh count.
Below is an animation that shows how it works with a window size of four requests. Requests start filling the window, then some get rejected. Once the window resets more requests are allowed.
#Redis data structure
STRING — one key per window, using
INCR to atomically bump the count and EXPIRE to auto-clean the key.#Use cases
- Simple API rate limiting (e.g. 100 requests per minute)
- Login attempt throttling
- Any scenario where simplicity and low memory matter more than boundary precision
#Code walkthrough
The full implementation lives in
server/components/rate-limiting/fixed-window.ts. Here's the core logic:Here's what's happening step by step:
- Window key derivation.
Math.floor(now / windowSeconds)converts the current timestamp into a window number. For a 10-second window at time1707000042, the window number is170700004. This becomes part of the key, so each window gets its own counter. - Atomic increment.
INCRcreates the key if it doesn't exist (starting at 1) or increments it. This is a single atomic Redis command, so concurrent requests can't produce a race condition — every caller gets a unique, sequential count. - Expiry on first request. When
count === 1this is the first request in a new window. We setEXPIREso the key auto-deletes after the window passes. This keeps memory bounded. - Retry-after calculation. If the request is denied, we check
TTLon the key to tell the client exactly how many seconds until the window resets.
#Trade-offs
- Pros: Minimal memory (one key per window), simple logic, fast (two Redis commands in the common case).
- Cons: Susceptible to boundary bursts. A client could send 10 requests at second 9 and another 10 at second 11 — 20 requests in 2 seconds while technically staying within a "10 per 10 seconds" limit, because the requests straddle two windows.
#2. Sliding window log
#How it works
Instead of counting requests in fixed buckets, log the exact timestamp of every request in a sorted set. On each new attempt, remove entries older than the window, then count what's left. If the count is below the limit, add the new entry. This gives you a true sliding window — no boundary bursts.
Below is an animation showing a sliding window log with a 5 entry window. A timestamp of each request is logged, and when the log fills to 5 more requests get rejected. Then the oldest entries start expiring as the window slides and more requests are accepted.
#Redis data structure
SORTED SET — the score is the request timestamp (milliseconds), and the value is a unique string (
timestamp:random). Redis commands used: ZREMRANGEBYSCORE, ZCARD, ZADD.#Use cases
- High-value APIs where boundary accuracy matters (payment processing, authentication)
- Scenarios where you need to know the exact request timestamps for auditing
- Low-to-medium request volume per client
#Code walkthrough
The full implementation lives in
server/components/rate-limiting/sliding-window-log.ts:When a request is denied, the code computes a precise retry-after by looking at the oldest entry:
Key details:
- Pruning.
ZREMRANGEBYSCOREremoves all entries with a score (timestamp) older than the window start. This keeps the set trimmed to only relevant requests. - Counting.
ZCARDreturns the number of remaining entries — the request count within the sliding window. - Unique members.
ZADDuses${now}:${Math.random()}as the member value. Sorted sets require unique members, so appending a random suffix prevents two requests at the same millisecond from colliding. - Retry-after. When denied, the code fetches the oldest entry's score and calculates when it will fall outside the window. That's the earliest moment a new request would be allowed.
#Trade-offs
- Pros: True sliding window with no boundary bursts. Precise retry-after calculations.
- Cons: Memory grows linearly with request volume (O(n) per client). For a limit of 10,000 requests per hour, each client's sorted set holds up to 10,000 entries. Not ideal for high-volume, high-cardinality rate limiting.
#3. Sliding window counter
#How it works
This is a hybrid approach. It keeps two fixed-window counters (current and previous) and computes a weighted average based on how far into the current window you are. The weight of the previous window decreases linearly as you move through the current window.
The animation below shows a sliding window counter that demonstrates how the algorithm smooths traffic across window boundaries. The rejections are scattered across the window when the weighted estimate (
prev * weight + curr) hits the limit of 4.#Redis data structure
STRING x2 — one key for the current window counter, one for the previous. Same
INCR + EXPIRE pattern as fixed window, but with two keys and a weighted formula.#Use cases
- Best middle ground for most apps — smoother than fixed window, far cheaper than the log
- API gateways and middleware where you want good accuracy without per-request storage
- High-volume rate limiting where memory matters
#Code walkthrough
The full implementation lives in
server/components/rate-limiting/sliding-window-counter.ts:If the estimate is under the limit, the code increments the current window:
Key details:
- Dual keys. Two STRING keys — one for the current window, one for the previous. This is all the state you need.
- The weighted formula.
prevCount * (1 - elapsed) + currentCountblends the two windows. At the start of a new window (elapsed = 0), the previous window counts fully. At the end (elapsed ≈ 1), the previous window counts almost nothing. This smooths the boundary spike that plagues fixed windows. - TTL of
windowSeconds * 2. The previous window's key must survive into the next window so it can be read for the weighted calculation. A TTL of twice the window size guarantees this. - Estimate-then-increment. The code checks the estimated count before incrementing. If the estimate already exceeds the limit, it denies immediately without writing anything. This avoids inflating the counter on denied requests.
#Trade-offs
- Pros: Low memory (two keys per client), smooths boundary bursts, fast (three to four Redis commands).
- Cons: The count is an approximation. In rare edge cases, the weighted estimate could let slightly more or fewer requests through than the exact limit. For most apps, this margin is negligible.
#4. Token bucket
#How it works
Imagine a bucket that holds tokens. Tokens refill at a steady rate (e.g. 1 per second). Each request removes one token. If the bucket is empty, the request is denied. The bucket has a maximum capacity, so tokens can't accumulate beyond a set limit. This allows short bursts (up to the bucket capacity) while enforcing a steady average rate.
The animation below demonstrates a token bucket that holds tokens. Incoming requests start to empty the bucket and reject when it is empty. Tokens replenish the bucket based on the refill rate.
#Redis data structure
HASH with two fields:
tokens (current token count) and last_refill (timestamp of the last refill). The entire refill-check-consume cycle runs inside a Lua script.#Why Lua?
The token bucket algorithm requires a read-modify-write sequence:
- Read current tokens and last refill time
- Calculate how many tokens to add based on elapsed time
- Decide whether to allow the request
- Write the updated state back
If you run these as separate Redis commands, two concurrent requests could both read the same token count, both decide they're allowed, and both write back — bypassing the limit. You might think a Redis transaction (
MULTI/EXEC) could solve this, but transactions don't let you branch on intermediate results. You can't read the hash inside a MULTI block and then conditionally decrement.A Lua script solves both problems. Redis executes the entire script atomically — no other command runs between the
HGETALL and the HSET. And you can use if/then logic inside the script to make decisions based on the data you just read.#Use cases
- API rate limiting where you want to allow short bursts (e.g. a mobile app that batches requests on launch)
- Payment or messaging APIs with a sustained average rate but tolerance for bursty traffic
- Per-user or per-API-key throttling
#Code walkthrough
The Lua script in
server/components/rate-limiting/token-bucket.ts:The TypeScript caller passes the script and parameters to Redis:
Key details:
HGETALLto load state. On the first request, the hash doesn't exist, sotokensdefaults tomax_tokens(a full bucket). On subsequent requests it reads the stored values.- Elapsed-time refill.
elapsed * refill_ratecalculates how many tokens accumulated since the last request.math.min(max_tokens, ...)caps it at the bucket capacity so tokens don't grow unbounded. - Consume one token. If at least one token is available, decrement and set
allowed = 1. - Persist and auto-clean.
HSETsaves the updated state.EXPIREsets a TTL so the key auto-deletes if the client goes idle. The TTL ismax_tokens / refill_rate + 1— the time it takes to fully refill, plus a buffer. - Caller passes
now. The timestamp comes from the app, not from Redis's clock. This makes the behavior deterministic and testable.
#Trade-offs
- Pros: Allows controlled bursts up to bucket capacity. Smooth long-term average rate. Single round trip (one
EVALcall). - Cons: More complex than counter-based approaches. Requires Lua scripting, which can be harder to debug. The refill calculation uses floating-point math, which needs care to avoid drift.
#5. Leaky bucket
#How it works
The leaky bucket is the inverse of the token bucket. Requests flow into the bucket, and the bucket drains (leaks) at a constant rate. If the bucket is full, new requests are rejected. This enforces a strict, steady output rate — no bursts allowed.
The animation below demonstrates the leaky bucket algorithm. The bucket stacks requests from bottom to top. Based on the drain rate, requests fall out of the bottom of the bucket. The bucket fills during a burst, rejects requests when full, and steadily drains to recover.
#Redis data structure
HASH with two fields:
level (current fill level) and last_leak (timestamp of the last drain calculation). Like the token bucket, this uses a Lua script for atomicity.#Why Lua?
The same reasoning applies here as with token bucket. The drain-check-fill cycle is a read-modify-write sequence that must happen atomically. Without Lua, concurrent requests could both read the same level, both decide there's room, and both increment — overfilling the bucket. A Lua script guarantees the entire operation runs as one atomic unit.
#Use cases
- Traffic shaping where you need a constant, predictable output rate
- Protecting downstream services that can only handle a fixed throughput
- Network-level rate limiting and queue management
#Code walkthrough
The Lua script in
server/components/rate-limiting/leaky-bucket.ts:The TypeScript caller follows the same pattern as the token bucket:
Key details:
- Drain calculation.
elapsed * leak_ratecomputes how much the bucket has leaked since the last request.math.max(0, level - leaked)ensures the level never goes negative. - Capacity guard. The check is
level + 1 <= capacity, notlevel < capacity. This avoids a subtle floating-point edge case: after draining, the level might be something like9.97due to fractional seconds.9.97 < 10is true, but adding 1 produces10.97, which overflows. Thelevel + 1 <= capacityform catches this. - Remaining uses
math.floor. Sincelevelis a float after draining,capacity - levelcould be fractional. Flooring gives the client a conservative integer for how many requests are left. - Auto-clean TTL. Same pattern as token bucket:
capacity / leak_rate + 1ensures the key expires after the bucket would fully drain if no new requests arrive.
#Trade-offs
- Pros: Smoothest possible output rate. Guarantees downstream services see a steady flow.
- Cons: Rejects bursty traffic even when the long-term average is within limits. A client that sends 5 requests at once might get some denied, even if they only send 5 requests total in a 10-second period. Also requires Lua scripting, so carries similar cons as mentioned for token buckets above.
#Comparison
| Algorithm | Redis type | Memory per client | Accuracy | Burst behavior | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed window | STRING | 1 key | Approximate | Allows 2x burst at boundaries | Low |
| Sliding window log | SORTED SET | O(n) entries | Exact | No bursts | Medium |
| Sliding window counter | STRING x2 | 2 keys | Near-exact | Smoothed boundaries | Low |
| Token bucket | HASH + Lua | 1 key (2 fields) | Exact | Allows controlled bursts | High |
| Leaky bucket | HASH + Lua | 1 key (2 fields) | Exact | No bursts (steady drain) | High |
#Choosing the right rate-limiting algorithm
- Need simplicity and low memory? Start with fixed window.
- Need boundary accuracy without per-request storage? Use sliding window counter.
- Need exact counts and can afford the memory? Use sliding window log.
- Want to allow bursts but cap the average rate? Use token bucket.
- Need strict, steady output rate? Use leaky bucket.
#Running the demo
Start Docker
This spins up Redis and the server. Alternatively you can spin up Redis and run the dev server:
Open
http://localhost:8080 in your browser. You'll see five cards — one for each algorithm. Each card has:- Send Request — fires a single request through the rate limiter and shows whether it was allowed or denied, along with remaining capacity.
- Burst 10 — sends 10 rapid requests in sequence. This is the fastest way to see an algorithm hit its limit.
- Reset All Counters — flushes all rate-limit keys from Redis so you can start fresh.
Try clicking Burst 10 on the fixed window card, then immediately clicking it again. You'll see the boundary burst problem in action. Then try the same thing on the sliding window log — no boundary burst.
#References
- Redis
INCRcommand — atomic counter increment used by the fixed window and sliding window counter - Redis sorted set commands —
ZADD,ZCARD,ZREMRANGEBYSCOREused by the sliding window log - Redis
EVALand Lua scripting — server-side scripting used by the token bucket and leaky bucket - Redis
EXPIREcommand — automatic key expiration used by all five algorithms - Redis Cloud free tier — get a free Redis database to try this tutorial
- Redis docs — comprehensive Redis documentation
