Upgrade Redis Enterprise for Kubernetes
Information about upgrading your Redis Enterprise cluster on Kubernetes.
| Redis Enterprise for Kubernetes |
|---|
Redis implements rolling updates for software upgrades in Kubernetes deployments. The upgrade process includes updating three components:
- Upgrade the Redis Enterprise operator
- Upgrade the Redis Enterprise cluster (REC)
- Upgrade Redis Enterprise databases (REDB)
To use OpenShift container platform CLI to upgrade your Redis Enterprise, see Upgrade Redis Enterprise with OpenShift CLI.
For all other Kubernetes distributions, see Upgrade Redis Enterprise for Kubernetes.
Upgrade compatibility
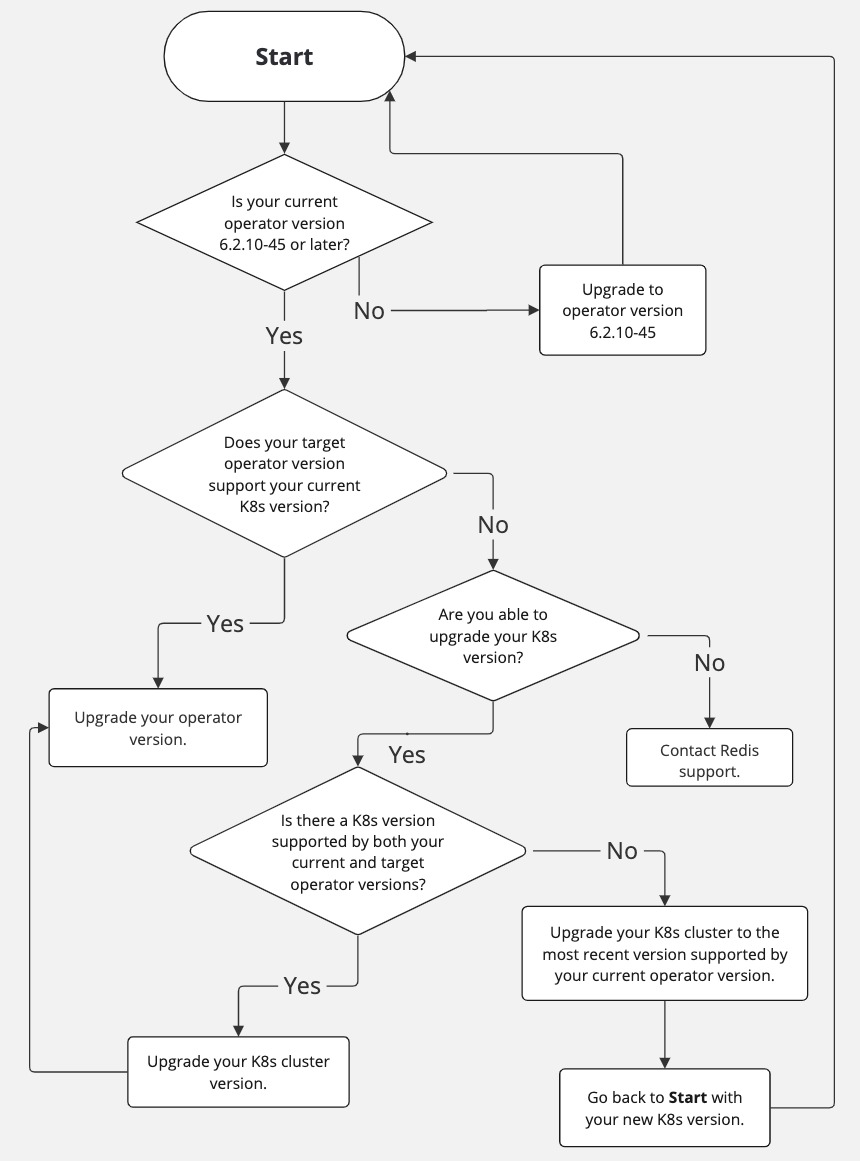
When upgrading, both your Kubernetes version and Redis operator version need to be supported at all times. When upgrading your Kubernetes version, you need to make sure both the current and target K8s version are supported by your Redis operator version. When upgrading your Redis operator version, you need make sure both the current and target operator versions are supported by your K8s version. This means if you are planning a large jump in versions, the upgrade might need to be done in multiple steps.
The flow chart below can help you decide if your upgrade requires multiple steps.
How does the REC upgrade work?
The Redis Enterprise cluster (REC) uses a rolling upgrade, meaning it upgrades pods one by one. Each pod is updated after the last one completes successfully. This helps keep your cluster available for use.
To upgrade, the cluster terminates each pod and deploys a new pod based on the new image. Before each pod goes down, the operator checks if the pod is a primary (master) for the cluster, and if it hosts any primary (master) shards. If so, a replica on a different pod is promoted to primary. Then when the pod is terminated, the API remains available through the newly promoted primary pod.
After a pod is updated, the next pod is terminated and updated. After all of the pods are updated, the upgrade process is complete.