Install on Kubernetes
Learn how to install RDI on Kubernetes
This guide explains how to use the RDI Helm chart to install on Kubernetes (K8s). You can also Install RDI on VMs.
The installation creates the following K8s objects:
- A K8s namespace named
rdi. You can also use a different namespace name if you prefer. - Deployments and services for the RDI operator, metrics exporter, and API server.
- A service account and RBAC resources for the RDI operator.
- A ConfigMap with RDI database details.
- Secrets with the RDI database credentials and TLS certificates.
- Other optional K8s resources such as ingresses that can be enabled depending on your K8s environment and needs.
You can use this installation on OpenShift and other K8s distributions including cloud providers' K8s managed clusters.
You can configure the RDI Helm chart to pull the RDI images from dockerhub or from your own private image registry.
Before you install
Complete the following steps before installing the RDI Helm chart:
-
Create the RDI database on your Redis Enterprise cluster.
-
Create a user for the RDI database if you prefer not to use the default password (see Access control for more information).
-
Download the RDI Helm chart tar file from the Redis download center (in the Modules, Tools & Integration category) .
export RDI_VERSION=1.16.1 wget https://redis-enterprise-software-downloads.s3.amazonaws.com/redis-di/rdi-$RDI_VERSION.tgz -
If you want to use a private image registry, prepare it with the RDI images.
Create the RDI database
RDI uses a database on your Redis Enterprise cluster to store its state information. Use the Redis Enterprise Cluster Manager UI to create the RDI database with the following requirements:
-
Redis Enterprise v6.4 or greater for the cluster.
-
For production, 250MB RAM with one primary and one replica is recommended, but for the quickstart or for development, 125MB and a single shard is sufficient.
-
If you are deploying RDI for a production environment then secure this database with a password and TLS.
-
Set the database's eviction policy to
noeviction. Note that you can't set this usingrladmin, so you must either do it using the admin UI or with the following REST API command:curl -v -k -d '{"eviction_policy": "noeviction"}' \ -u '<USERNAME>:<PASSWORD>' \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -X PUT https://<CLUSTER_FQDN>:9443/v1/bdbs/<BDB_UID> -
Set the database's data persistence to AOF - fsync every 1 sec. Note that you can't set this using
rladmin, so you must either do it using the admin UI or with the following REST API commands:curl -v -k -d '{"data_persistence":"aof"}' \ -u '<USERNAME>:<PASSWORD>' \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X PUT https://<CLUSTER_FQDN>:9443/v1/bdbs/<BDB_UID> curl -v -k -d '{"aof_policy":"appendfsync-every-sec"}' \ -u '<USERNAME>:<PASSWORD>' \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -X PUT https://<CLUSTER_FQDN>:9443/v1/bdbs/<BDB_UID> -
Ensure that the RDI database is not clustered. RDI will not work correctly if the RDI database is clustered (but note that the target database can be clustered without any problems).
If the Database clustering option is checked when you create the RDI database (as shown below), you must uncheck it before proceeding.
You can check if your RDI database is clustered from its Configuration tab in the Redis Enterprise console. The Database clustering option should be set to None, as shown in the following screenshot:
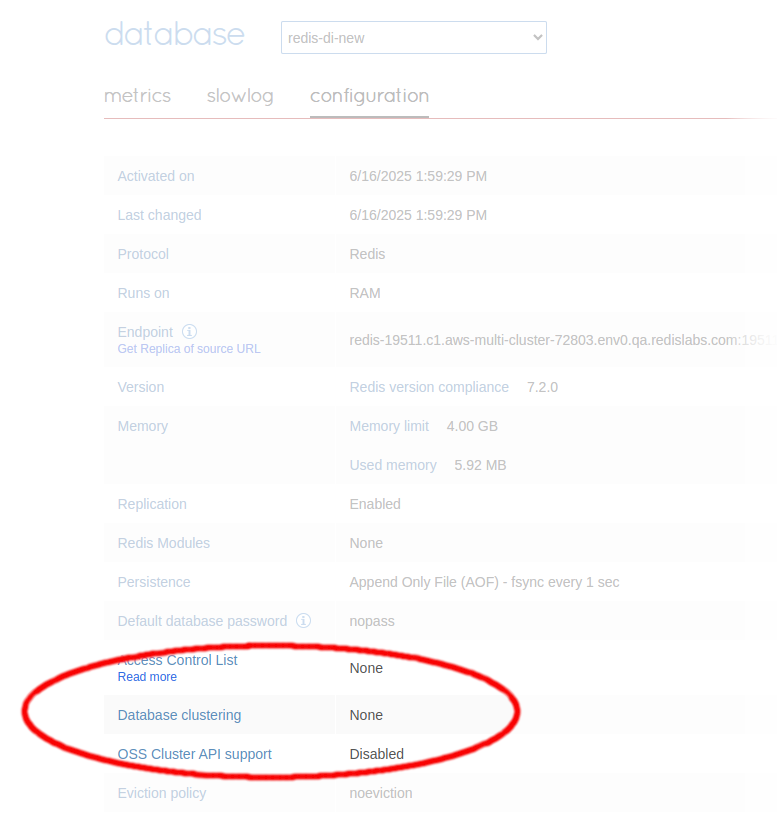
If you find the database has been clustered by mistake, you must create a new database with clustering disabled before continuing with the RDI installation.
You should then provide the details of this database in the values.yaml
file as described below.
Using a private image registry
Add the RDI images from dockerhub to your local registry. You need the following RDI images with tags matching the RDI version you want to install:
- redis/rdi-api
- redis/rdi-operator
- redis/rdi-monitor
- redis/rdi-processor
- redis/rdi-collector-api
- redis/rdi-collector-initializer
If you plan to use Spanner as a source for your pipeline, you’ll need an additional image.: redis/rdi-flink-collector.
In addition, the RDI Helm chart uses the following 3rd party images:
- redislabs/debezium-server:3.0.8.Final-rdi.1,
based on
quay.io/debezium/server/3.0.8.Finalwith minor modifications: Debezium, an open source distributed platform for change data capture. - redis/reloader:v1.1.0, originally
ghcr.io/stakater/reloader:v1.1.0: Reloader, a K8s controller to watch changes to ConfigMaps and Secrets and do rolling upgrades. - redis/kube-webhook-certgen:v20221220-controller-v1.5.1-58-g787ea74b6,
originally
registry.k8s.io/ingress-nginx/kube-webhook-certgen/v20221220-controller-v1.5.1-58-g787ea74b6: kube-webhook-certgen, K8s webhook certificate generator and patcher.
The example below shows how to specify the registry and image pull secret in your
rdi-values.yaml file for the Helm chart:
global:
# Global image settings.
# If using a private image registry, update the default values accordingly.
image:
registry: your-registry
repository: your-repository # If different from "redis"
# Image pull secrets to be used when using a private image registry.
imagePullSecrets:
- name: your-secret-name
# ...
# Configuration of the reloader.
reloader:
reloader:
# ...
deployment:
image:
name: my-registry.com/my-repo/reloader
#...
To pull images from a private image registry, you must provide the image pull secret and in some cases also set the permissions. Follow the links below to learn how to use a private registry with:
- Rancher
- OpenShift
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Supported versions of Kubernetes and OpenShift
RDI only supports versions of Kubernetes and OpenShift that have not yet reached end-of-life (EOL). See the Kubernetes and OpenShift lifecycle pages for the latest updates.
Install the RDI Helm chart
-
Scaffold the default
values.yamlfile from the chart into a localrdi-values.yamlfile:helm show values rdi-<tag>.tgz > rdi-values.yaml -
Open the
rdi-values.yamlfile you just created, change or add the appropriate values for your installation, and delete the values you have not changed to use their default values. See Thevalues.yamlfile for more details. -
Run the
helm upgrade --installcommand:helm upgrade --install rdi rdi-<tag>.tgz -f rdi-values.yaml -n rdi --create-namespaceNote:The above command will install RDI in a namespace calledrdi. If you want to use a different namespace, pass the option-n <custom-namespace>to thehelm installcommand instead.
The values.yaml file
The values.yaml file inside the
Helm chart contains the values you can set for the RDI Helm installation.
See the comments by each value for more information about the values you may need to add or change
depending on your use case.
At a minimum, you must set the values of connection.host, connection.port, and connection.password
to enable the basic connection to the RDI database.
You must also set api.jwtKey, RDI uses this value to encrypt the
JSON web token (JWT) token used by RDI API. Best practice is
to generate a value containing 32 random bytes of data (equivalent to 256
bits) and then encode this value as ASCII characters. Use the following
command to generate the random key from the
urandom special file:
head -c 32 /dev/urandom | base64
If you use TLS to connect to the RDI database, you must set the
CA certificate content in connection.ssl.cacert (for TLS). In addition, if you
also use mTLS, you must set the client certificate and private key contents in
connection.ssl.cert, and connection.ssl.key.
-
You can add the certificate content directly in the
rdi-values.yamlfile as follows:connection: ssl: enabled: true cacert: | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ... -----END CERTIFICATE----- cert: | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- ... -----END CERTIFICATE----- key: | -----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- ... -----END PRIVATE KEY----- -
Alternatively, you can use the
--set-fileargument to set these values to the content of your certificate files as follows:helm upgrade --install rdi rdi-<tag>.tar.gz -f rdi-values.yaml -n rdi --create-namespace \ --set connection.ssl.enabled=true \ --set-file connection.ssl.cacert=<path-to-CA-certificate> \ --set-file connection.ssl.cert=<path-to-client-certificate> \ --set-file connection.ssl.key=<path-to-client-key>
If you are deploying to OpenShift, you must
set global.openshift to true:
global:
# Indicates whether the deployment is intended for an OpenShift environment.
openShift: true
Set global.securityContext.runAsUser and
global.securityContext.runAsGroup to the appropriate values for your
OpenShift environment.
global:
# Container default security context.
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/security-context/#set-the-security-context-for-a-container
securityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
# On OpenShift, user and group 1000 are usually not allowed.
# If using OpenShift, set runAsUser and runAsGroup to values in your project's user and group ranges.
# You can examine the latter via `oc get projects <rid-project-name> -o yaml | grep "openshift.io/sa.scc"`
runAsUser: 1000701234
runAsGroup: 1000701234
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
The default OpenShift Security Context Constraints (SCCs)
will not allow RDI to run if global.securityContext.runAsUser
and global.securityContext.runAsGroup have their default values of 1000.
You must edit your rdi-values.yaml file to ensure these values are
in the valid range for your OpenShift environment.
Use the following OpenShift CLI command to find the user and group ranges for your project:
oc get projects <rid-project-name> -o yaml | grep "openshift.io/sa.scc"
Check the installation
To verify the status of the K8s deployment, run the following command:
helm list -n rdi
The output looks like the following. Check that the rdi release is listed.
With RDI 1.8.0 or later, check that the default release is also listed.
NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
default rdi 1 2025-05-08 ... deployed pipeline-0.1.0 <tag>
rdi rdi 3 2025-05-08 ... deployed rdi-1.0.0
Also, check that all pods have Running status:
kubectl get pod -n rdi
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
collector-api-<id> 1/1 Running 0 29m
rdi-api-<id> 1/1 Running 0 29m
rdi-metric-exporter-<id> 1/1 Running 0 29m
rdi-operator-<id> 1/1 Running 0 29m
rdi-reloader-<id> 1/1 Running 0 29m
You can verify that the RDI API works by adding a connection to the RDI API server to Redis Insight.
Using ingress controllers
You must ensure that an appropriate
ingress controller
is available in your K8s cluster to expose the RDI API service via the K8s
Ingress
resource. Follow the documentation of your cloud provider or of
the ingress controller to install the controller correctly.
Using the nginx ingress controller on AKS
On AKS, if you want to use the open source
nginx
ingress controller
rather than the
AKS application routing add-on,
follow the AKS documentation for
creating an unmanaged ingress controller.
Specifically, ensure that one or both of the following Helm chart values is set:
controller.service.annotations."service\.beta\.kubernetes\.io/azure-load-balancer-health-probe-request-path"=/healthzcontroller.service.externalTrafficPolicy=Local
Prepare your source database
Before deploying a pipeline, you must configure your source database to enable CDC. See the Prepare source databases section to learn how to do this.
Deploy a pipeline
When the Helm installation is complete and you have prepared the source database for CDC, you are ready to start using RDI. Use Redis Insight to configure and deploy your pipeline (see RDI in Redis Insight for full details on how to do this).
Uninstall RDI
If you want to remove your RDI K8s installation, first run
the following commands. (If you installed RDI into a custom namespace then
replace rdi with the name of your namespace.)
kubectl delete pipeline default -n rdi
helm uninstall rdi -n rdi
kubectl delete namespace rdi
kubectl delete pipeline default -n rdi is only needed for RDI 1.8.0 or above.If you also want to delete the keys from your RDI database, connect to it with
redis-cli and run a
FLUSHALL command.