Install on VMs
Learn how to install RDI on one or more VMs
This guide explains how to install Redis Data Integration (RDI) on one or more VMs and integrate it with your source database. You can also Install RDI on Kubernetes.
Create the RDI database
RDI uses a database on your Redis Enterprise cluster to store its state information. Use the Redis Enterprise Cluster Manager UI to create the RDI database with the following requirements:
-
Redis Enterprise v6.4 or greater for the cluster.
-
For production, 250MB RAM with one primary and one replica is recommended, but for the quickstart or for development, 125MB and a single shard is sufficient.
-
If you are deploying RDI for a production environment then secure this database with a password and TLS.
-
Set the database's eviction policy to
noeviction. Note that you can't set this usingrladmin, so you must either do it using the admin UI or with the following REST API command:curl -v -k -d '{"eviction_policy": "noeviction"}' \ -u '<USERNAME>:<PASSWORD>' \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -X PUT https://<CLUSTER_FQDN>:9443/v1/bdbs/<BDB_UID> -
Set the database's data persistence to AOF - fsync every 1 sec. Note that you can't set this using
rladmin, so you must either do it using the admin UI or with the following REST API commands:curl -v -k -d '{"data_persistence":"aof"}' \ -u '<USERNAME>:<PASSWORD>' \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X PUT https://<CLUSTER_FQDN>:9443/v1/bdbs/<BDB_UID> curl -v -k -d '{"aof_policy":"appendfsync-every-sec"}' \ -u '<USERNAME>:<PASSWORD>' \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -X PUT https://<CLUSTER_FQDN>:9443/v1/bdbs/<BDB_UID> -
Ensure that the RDI database is not clustered. RDI will not work correctly if the RDI database is clustered (but note that the target database can be clustered without any problems).
If the Database clustering option is checked when you create the RDI database (as shown below), you must uncheck it before proceeding.
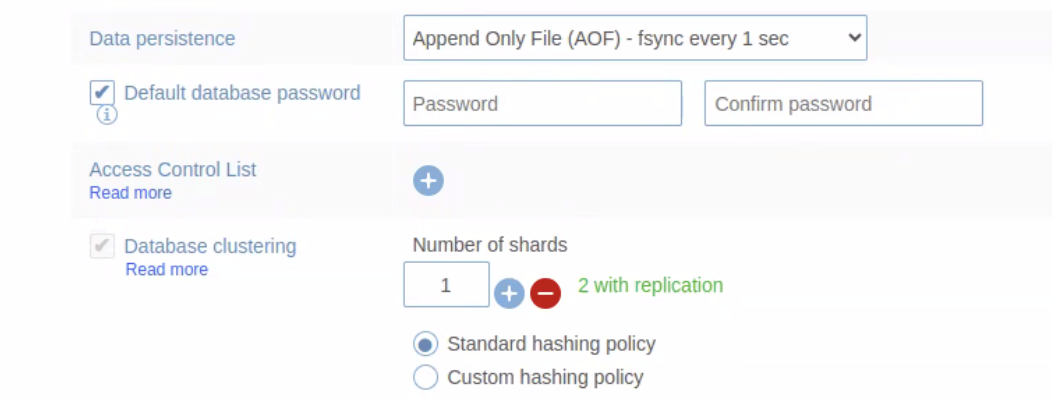
You can check if your RDI database is clustered from its Configuration tab in the Redis Enterprise console. The Database clustering option should be set to None, as shown in the following screenshot:
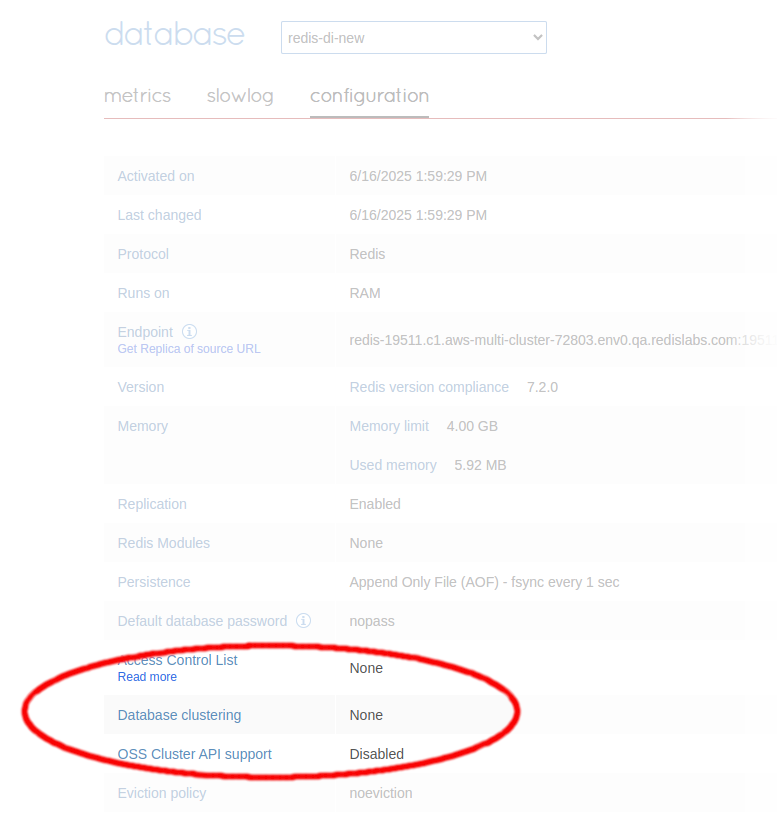
If you find the database has been clustered by mistake, you must create a new database with clustering disabled before continuing with the RDI installation.
Hardware sizing
RDI is mainly CPU and network bound. Each of the RDI VMs should have at least:
- CPU: A minimum of 4 CPU cores. You should consider adding 2-6 extra cores on top of this if your dataset is big and you want to ingest the baseline snapshot as fast as possible.
- RAM: 8GB
- Disk: On top of the OS footprint,
RDI requires 20GB in the
/varfolder and 1GB in the/optfolder (to store the log files). This allows space for upgrades. - Network interface: 10GB or more.
VM Installation Requirements
You would normally install RDI on two VMs for High Availability (HA) but you can also install just one VM if you don't need this. For example, you might not need HA during development and testing.
You can't install RDI on a host where a Redis Enterprise cluster
is also installed, due to incompatible network rules. If you want to install RDI on a
host that you have previously used for Redis Enterprise then you must
use iptables to
"clean" the host before installation with the following command line:
sudo iptables-save | awk '/^[*]/ { print $1 }
/^:[A-Z]+ [^-]/ { print $1 " ACCEPT" ; }
/COMMIT/ { print $0; }' | sudo iptables-restore
You may encounter problems if you use iptables v1.6.1 and earlier in
nftables mode. Use iptables versions later than v1.6.1 or enable the iptables
legacy mode with the following commands:
sudo update-alternatives --set iptables /usr/sbin/iptables-legacy
sudo update-alternatives --set ip6tables /usr/sbin/ip6tables-legacy
Also, iptables versions 1.8.0-1.8.4 have known issues that can prevent RDI
from working, especially on RHEL 8. Ideally, use iptables v1.8.8, which is
known to work correctly with RDI.
The supported OS versions for RDI are:
- RHEL 8 or 9
- Ubuntu 20.04, 22.04, or 24.04
You must run the RDI installer as a privileged user because it installs containerd and registers services. However, you don't need any special privileges to run RDI processes for normal operation.
RDI has a few requirements for cloud VMs that you must implement before running the RDI installer, or else installation will fail. The following sections give full pre-installation instructions for RHEL and Ubuntu.
RHEL
We recommend you turn off
firewalld
before installation using the command:
sudo systemctl disable firewalld --now
However, if you do need to use firewalld, you must add the following rules:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=443/tcp # RDI API
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=6443/tcp # kube-apiserver
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=trusted --add-source=10.42.0.0/16 # Kubernetes pods
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=trusted --add-source=10.43.0.0/16 # Kubernetes services
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
If you have nm-cloud-setup.service enabled, you must disable it and reboot the
node with the following commands:
sudo systemctl disable nm-cloud-setup.service nm-cloud-setup.timer
sudo reboot
Ubuntu
We recommend you turn off
Uncomplicated Firewall (ufw)
before installation with the command:
sudo ufw disable
However, if you do need to use ufw, you must add the following rules:
sudo ufw allow 443/tcp # RDI API
sudo ufw allow 6443/tcp # kube-apiserver
sudo ufw allow from 10.42.0.0/16 to any # Kubernetes pods
sudo ufw allow from 10.43.0.0/16 to any # Kubernetes services
sudo ufw reload
Installation steps
Follow the steps below for each of your VMs.
RDI installs executables by default in the /var partition, so you must
ensure it is mounted without the noexec option. Use the following command to
find any partitions mounted with the noexec option:
mount | grep noexec
If your /var partition is listed in the output from this command, you must remount
it without the noexec option. See
Using the mount command in the Red Hat documentation to learn how to remount a partition.
-
Download the RDI installer from the Redis download center (from the Modules, Tools & Integration category) and extract it to your preferred installation folder.
export RDI_VERSION=1.16.1 wget https://redis-enterprise-software-downloads.s3.amazonaws.com/redis-di/rdi-installation-$RDI_VERSION.tar.gz tar -xvf rdi-installation-$RDI_VERSION.tar.gz -
Go to the installation folder:
cd rdi_install/$RDI_VERSION -
Run the
install.shscript as a privileged user:sudo ./install.shNote:RDI uses K3s as part of its implementation. By default, the installer installs K3s in the
/var/libdirectory, but this might be a problem if you have limited space in/varor your company policy forbids you to install there. You can select a different directory for the K3s installation using the--installation-diroption withinstall.sh:sudo ./install.sh --installation-dir <custom-installation-directory>Advanced: You can also pass custom K3s parameters to the installer using the
INSTALL_K3S_EXECenvironment variable. For example, to set the kubeconfig file permissions to be readable by all users:sudo INSTALL_K3S_EXEC='--write-kubeconfig-mode=644' ./install.shYou can combine multiple K3s options in the
INSTALL_K3S_EXECvariable. See the K3s documentation for a full list of available options.Warning:Only modify K3s parameters if you understand exactly what you are changing and why. Incorrect K3s configuration can cause RDI installation to fail or result in an unstable deployment.
The RDI installer collects all necessary configuration details and alerts you to potential issues, offering options to abort, apply fixes, or provide additional information. Once complete, it guides you through creating secrets and setting up your pipeline.
It is strongly recommended to specify a hostname rather than an IP address for connecting to your RDI database, for the following reasons:
- Any DNS resolution issues will be detected during the installation rather than later during pipeline deployment.
- If you use TLS, your RDI database CA certificate must contain the hostname you specified either as a common name (CN) or as a subject alternative name (SAN). CA certificates usually don't contain IP addresses.
If you specify localhost as the address of the RDI database server during
installation then the connection will fail if the actual IP address changes for the local
VM. For this reason, we recommend that you don't use localhost for the address. However,
if you do encounter this problem, you can fix it using the following commands on the VM
that is running RDI itself:
sudo k3s kubectl delete nodes --all
sudo service k3s restart
After the installation is finished, RDI is ready for use.
Supply cloud DNS information
If you are using Amazon Route 53, Google Cloud DNS, or Azure DNS then you must supply the installer with the nameserver IP address during installation. The table below shows the appropriate IP address for each cloud provider:
| Platform | Nameserver IP |
|---|---|
| Amazon Route 53 | 169.254.169.253 |
| Google Cloud DNS | 169.254.169.254 |
| Azure DNS | 168.63.129.16 |
If you are using Route 53, you should first check that your VPC is configured to allow it. See DNS attributes in your VPC in the Amazon docs for more information.
Installing with High Availability
To install RDI with High Availability (HA), perform the Installation steps on two different VMs. The first VM will automatically become the active (primary) instance, while the second VM will become the passive (secondary) one. When starting the RDI installation on the second VM, the installer will detect that the RDI database is already in use and ask you to confirm that you intend to install RDI with HA.
After the installation is complete, you must set the source and target database secrets
on both VMs as described in Deploy a pipeline. If you use redis-di to deploy your configuration, you only need to do this on one of the VMs, not both.
In a High Availability setup, the RDI pipeline is only active on the primary instance (VM). The two RDI instances will use the RDI database for leader election. If the primary instance fails to renew the lease in the RDI database, it will lose the leadership and a failover to the secondary instance will take place. After the failover, the secondary instance will become the primary one, and the RDI pipeline will be active on that VM.
You may find it useful to trigger a failover deliberately to check that RDI is correctly configured to handle it. See Test HA failover to learn how to do this.
Prepare your source database
Before deploying a pipeline, you must configure your source database to enable CDC. See the Prepare source databases section to learn how to do this.
Deploy a pipeline
When the installation is complete, and you have prepared the source database for CDC, you are ready to start using RDI. See the guides on how to configure and deploy RDI pipelines for more information. You can also configure and deploy a pipeline using Redis Insight. See RDI in Redis Insight for full details on how to connect to RDI and deploy pipelines.
Uninstall RDI
If you want to remove your RDI installation, go to the installation folder and run the uninstall script as a privileged user:
sudo ./uninstall.sh
The script will ask if you are sure before proceeding:
This will uninstall RDI and its dependencies, are you sure? [y, N]
If you type anything other than "y" here, the script will abort without making any changes to RDI or your source database.