Create a Redis Flex database
Shows how to create an Redis Flex database on Redis Cloud and describes the best use cases for Redis Flex.
| Redis Cloud |
|---|
Redis Flex databases have a tiered solid state drive (SSD) and RAM architecture. Using SSDs instead of RAM significantly reduces infrastructure costs, which means developers can build applications that require large datasets using the same Redis API.
Redis Flex databases are compatible with most existing Redis applications, except for applications that use Search and Query and Time Series.
Redis Flex is available on both Redis Cloud Essentials and Redis Cloud Pro.
Redis Flex use cases
The benefits associated with Redis Flex are dependent on the use case.
Redis Flex is ideal when your:
- working set is significantly smaller than your dataset (high RAM hit rate)
- average key size is smaller than average value size
- most recent data is the most frequently used (high RAM hit rate)
Redis Flex is not recommended for:
- Broad access patterns (any value could be pulled into RAM)
- Large working sets (working set is stored in RAM)
- Frequently moved data (moving to and from RAM too often can impact performance)
Redis Flex is not intended to be used for persistent storage.
Where is my data?
When using Redis Flex, RAM storage holds:
- Key indexes
- Dictionaries
- Hot data (working set), including frequently accessed keys and values
All data is accessed through RAM. If a key or value in flash memory is accessed, it becomes part of the working set and is moved to RAM. This data is referred to as "hot data".
Inactive or infrequently accessed data is referred to as "warm data" and stored in flash memory. When more space is needed in RAM, warm keys and values are moved from RAM to flash storage.
Create a Redis Flex database on Redis Cloud Essentials
Before creating a Redis Cloud database, you need to create an account.
To create a database in your Redis Cloud account:
-
Sign in to the Redis Cloud console.
-
Select the New database button.

This displays the Create database screen.
-
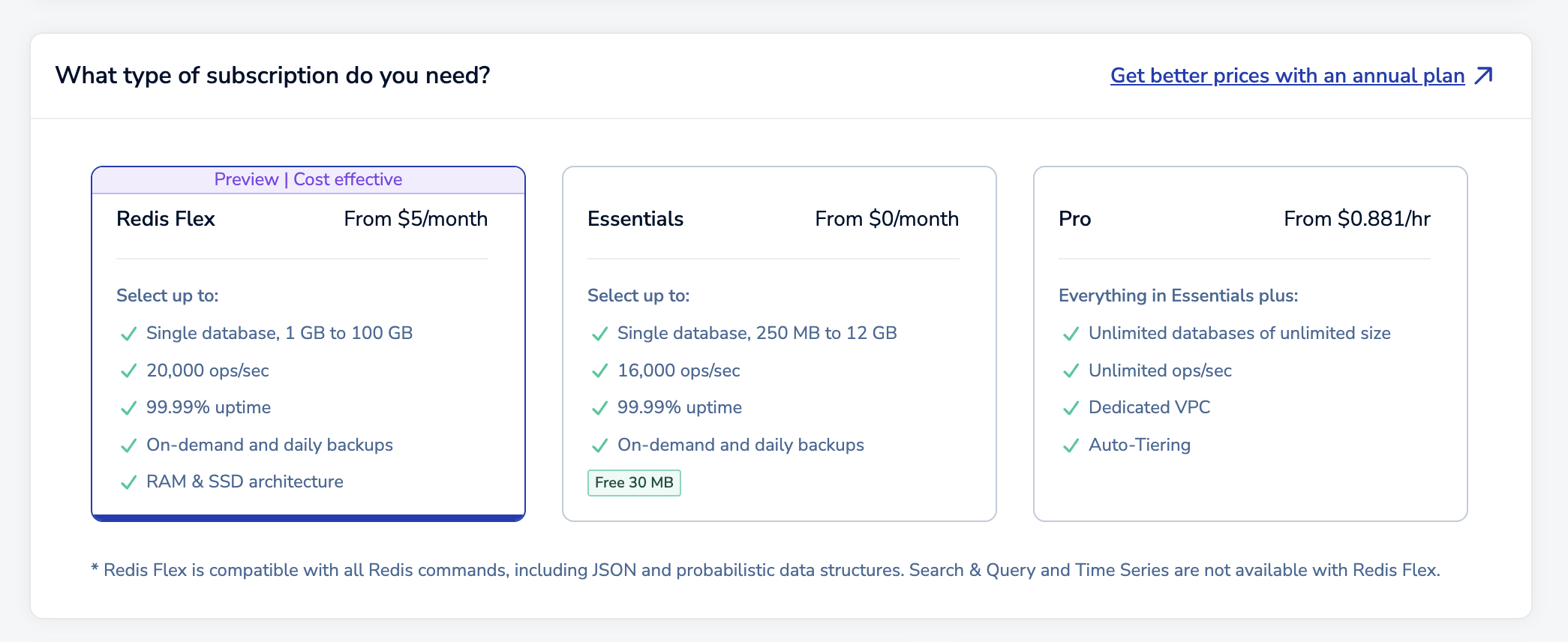
Select the type of subscription you need. For this guide, select Essentials - Flex.
 Note:
Note:This guide shows how to create a Redis Flex database on Redis Cloud Essentials.
- If you'd rather create a Redis on RAM Essentials database, see Create an Essentials database.
- If you'd rather create a Pro database, see Create a Pro database with a new subscription.
- If you already have a Pro subscription and want to add a database to it, see Create a Pro database in an existing subscription.
After you select Essentials - Flex, the rest of the database details will appear.
-
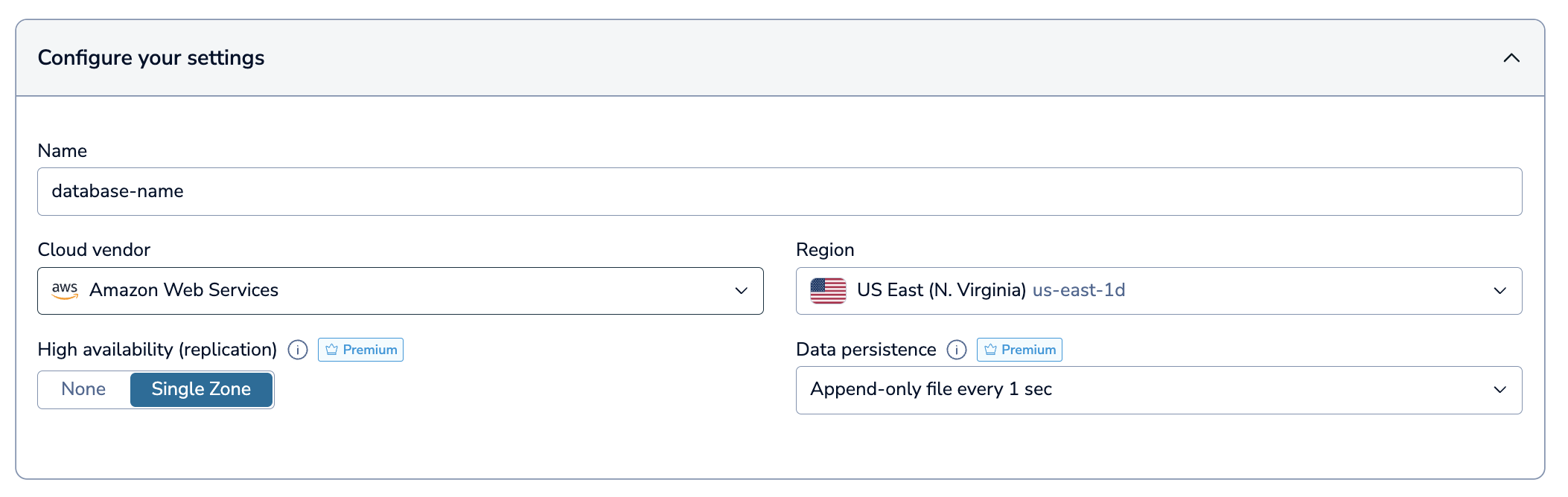
Redis will generate a database name for you. If you want to change it, you can do so in the Database name field.
-
Choose a Region on Amazon Web Services for your database. See Supported regions for a list of supported regions by cloud vendor.
-
Choose your High availability (replication) settings from the list.
Redis Cloud supports the following high availability settings with Redis Flex:
- None: You will have a single copy of your database without replication.
- Single-Zone: Your database will have a primary and a replica located in the same cloud zone. If anything happens to the primary, the replica takes over and becomes the new primary.
See High availability for more information about these settings.
-
Choose your Data persistence settings from the list.
Redis Cloud supports the following Data persistence options:
-
An Append-Only File maintains a record (sometimes called a redo log or journal) of write operations. This allows the data to be restored by using the record to reconstruct the database up to the point of failure. For Essentials databases, Redis updates the Append-Only file every second.
-
A Snapshot is a copy of the in-memory database, taken at periodic intervals (one, six, or twelve hours). You can restore data to the snapshot's point in time.
See Data persistence for more information about these settings.
-
-
Select the Database version you want to use.
-
Select your desired memory limit.
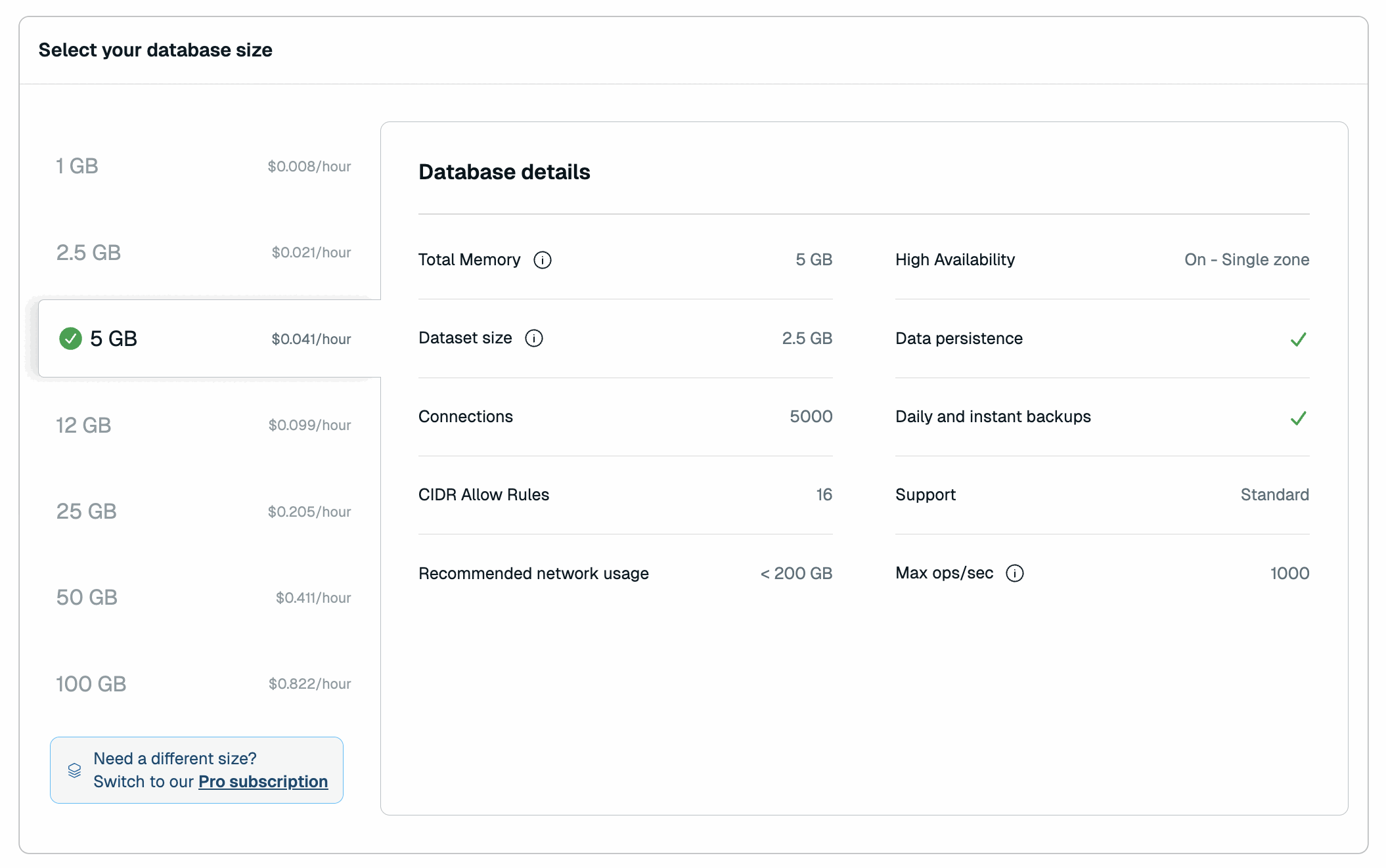
For a comparison of available plans, see Redis Cloud Essentials plans.
-
Enter your payment details.
If you haven't previously entered a payment method, use the Add Credit Card button to add one.

If you have not already added a business address to your account, you must enter one. Redis uses your business address for communication, invoicing, and tax purposes.
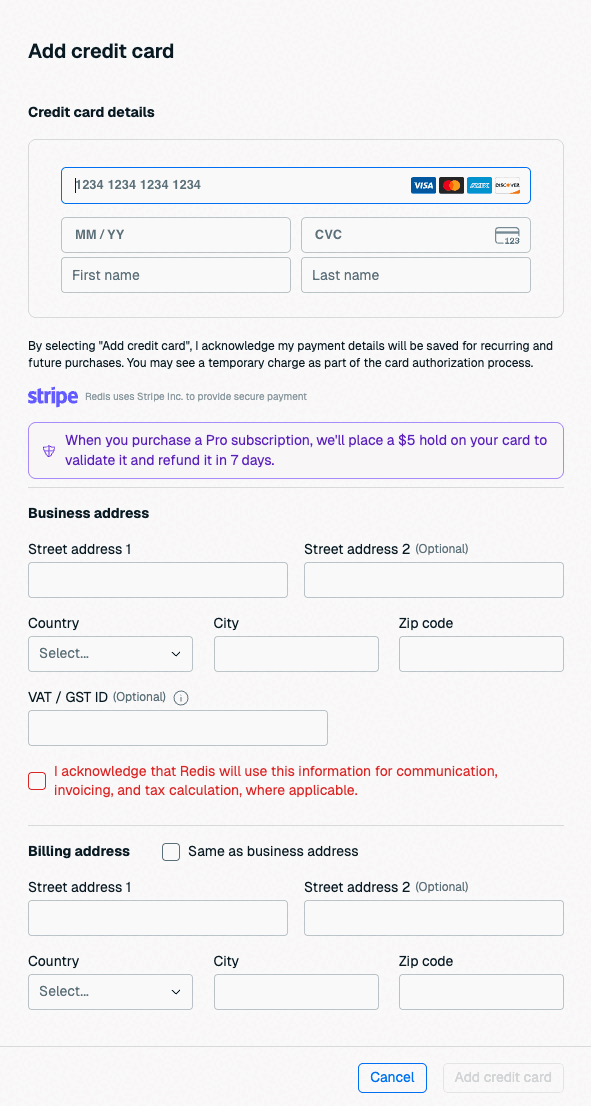
If you already have a business address, you don't need to enter one here. See Account settings to learn how to update your business address.

If the card's billing address is the same as your account's business address, select Same as business address to fill the billing address with your business address details.
-
Select Confirm & pay to create your database.

When you create your database, there's a brief pause while your request is processed and then the Database details page appears.
Create a Redis Flex database on Redis Cloud Pro
To create a Redis Flex database on Redis Cloud Pro, create a new Pro database with custom settings.
In the Advanced options of the Setup tab, select Redis Flex.

Continue with the instructions to create your database.